461 DELIVERING SUSTAINABLE SOLUTIONS TO IMPROVE WELLBEING
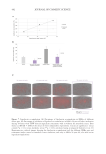
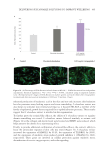
As shown in Figure 6, a significant decrease (45.3%) in formation of AGEs in tubo
(antiglycation effect) for the active ingredient was observed with respect to the control,
which suggests an anti-inflammatory and rejuvenating effect.
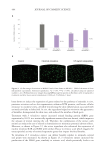
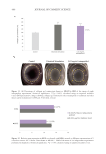
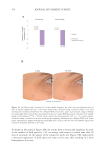
To check if the active ingredient could counteract the garbaging process, lipofuscin
accumulation was analyzed by measuring the fluorescence signal as lipofuscin is an
autofluorescent pigment commonly used as an indicator of waste accumulation. As
shown in Figure 7A &C, lipofuscin accumulation was confirmed to increase with aging
in HEKa in a linear way. In all HEKa ages, the metabolic stress induced an increase in
lipofuscin accumulation compared to its respective control. The older the HEKa are,
the larger the increase between basal and metabolic stress conditions. The treatment
with THW biotech ingredient concentrates in older keratinocytes significantly reduced
lipofuscin accumulation in vitro by 50.0% with respect to the control, as well as a 54.0%
reduction when induced by metabolic stress, which is equivalent to cells behaving
younger (Figure 7B, C).
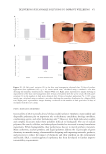
To further confirm the anti-inflammatory capacity of the active ingredient, IL1alpha, a
proinflammatory cytokine released by the RAGE-NF-kB pathway, was measured and
compared with the use of a specific RAGE antibody that blocks RAGE activity. As shown in
Figure 8, the THW biotech ingredient concentrate reduced the release of proinflammatory
IL1alpha in vitro by 12.4% with respect to the control as well as reductions of 20.0%
(at 10 µg/mL) and 27.7% (at 100 µg/mL) when induced by metabolic stress and in a
statistically significant and similar manner to the use of a specific RAGE antibody. These
results indicate that the active ingredient counteracts the RAGE-NF-kB activity, which
reduces the proinflammatory skin reaction.
Figure 6. Percentage of inhibition of AGE formation in tubo after incubation during 3 days with THW
biotech ingredient concentrate. Data shown as MEAN ± SEM of the mean of 4 independent experiments.
Statistical significance versus control: ***p 0.001, calculated using an unpaired student’s t test.
As shown in Figure 6, a significant decrease (45.3%) in formation of AGEs in tubo
(antiglycation effect) for the active ingredient was observed with respect to the control,
which suggests an anti-inflammatory and rejuvenating effect.
To check if the active ingredient could counteract the garbaging process, lipofuscin
accumulation was analyzed by measuring the fluorescence signal as lipofuscin is an
autofluorescent pigment commonly used as an indicator of waste accumulation. As
shown in Figure 7A &C, lipofuscin accumulation was confirmed to increase with aging
in HEKa in a linear way. In all HEKa ages, the metabolic stress induced an increase in
lipofuscin accumulation compared to its respective control. The older the HEKa are,
the larger the increase between basal and metabolic stress conditions. The treatment
with THW biotech ingredient concentrates in older keratinocytes significantly reduced
lipofuscin accumulation in vitro by 50.0% with respect to the control, as well as a 54.0%
reduction when induced by metabolic stress, which is equivalent to cells behaving
younger (Figure 7B, C).
To further confirm the anti-inflammatory capacity of the active ingredient, IL1alpha, a
proinflammatory cytokine released by the RAGE-NF-kB pathway, was measured and
compared with the use of a specific RAGE antibody that blocks RAGE activity. As shown in
Figure 8, the THW biotech ingredient concentrate reduced the release of proinflammatory
IL1alpha in vitro by 12.4% with respect to the control as well as reductions of 20.0%
(at 10 µg/mL) and 27.7% (at 100 µg/mL) when induced by metabolic stress and in a
statistically significant and similar manner to the use of a specific RAGE antibody. These
results indicate that the active ingredient counteracts the RAGE-NF-kB activity, which
reduces the proinflammatory skin reaction.
Figure 6. Percentage of inhibition of AGE formation in tubo after incubation during 3 days with THW
biotech ingredient concentrate. Data shown as MEAN ± SEM of the mean of 4 independent experiments.
Statistical significance versus control: ***p 0.001, calculated using an unpaired student’s t test.