390 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
The mechanisms by which the above type of moisturizing ingredients provide benefit from
wash-off systems vary significantly depending upon the nature of the ingredients. Since these
mechanisms are likely to be similar to their function from leave-on systems, they will be
discussed in later sections. It should be noted that there are differences between leave-on
and wash-off systems. The presence of high levels of surfactants and skin hydration under
cleansing conditions often helps to deliver certain actives rapidly into deeper layers. However,
the time of contact during cleansing is limited, and therefore the overall benefits from wash-
off systems will always be much lower than what can be expected from leave-on systems.
OTHER INGREDIENTS IN CLEANSERS
In addition to surfactants, other ingredients present in cleansers include polymers,
preservatives, pH modifiers, skin benefit agents, and fragrances.
POLYMERS
Polymers are generally used for structuring formulations, conditioning skin and hair, or for
deposition emollient and occlusive materials onto skin and hair. Polymers, because of their
high molecular weight, do not penetrate through the human SC and do not pose any major
threat to the skin barrier. Role of polymers in cosmetics has been reviewed by Lochhead,57
and a detailed review of polymers is beyond the scope of this paper. Cationic polymers
help to enhance the deposition of droplets and dispersed materials on skin and hair, as
both these surfaces are negatively charged under cleansing conditions. Polymers adsorbed
on skin and hair by themselves also can modify their wet and dry sensory and lubrication
properties. Silicone polymers, especially crosslinked silicone elastomers, are well known for
their consumer desired silky feel on skin and hair.58
Minimize Damage
Compensate for
surfactant damage
Provide posig415ve
benefits
Reduce
protein
damage
Reduce
loss of
NMFs
Reduce
lipid
damage
Mild surfactants
(Lower micellar
charge density-
large head-groups,
low acg415ve levels)
e.g. Isethionates,
Glycinates
SLES-Betaine
Combos (SLS-free),
Other aminoacid based
surfactants
Pre-saturate
surfactant
micelles with
sacrificial lipids
e.g. fag425y acids &
sterols in Bars &
Liquids
Replenish
NMFs/
humectants
Replenish
lipids
Provide
masking/
occlusion
for barrier
repair
Provide
“nutrients”/
Pro-lipids
for maintaining/
rebuilding
healthy corneum
Deposit /
deliver
Glycerol, PCA
&amino acids
during
cleansing
Deposit/
deliver
fag425y acids
&sterols
during
cleansing
Deposit
PJ/triglyceride
oils during
cleansing
Deliver
acg415ves that can
penetrate into
deeper layers &
enhance healthy
barrier rebuilding,
e.g. Esseng415al
fag425y acids,
Strategies for Mild and Moisturizing Cleanser Technologies
Maintain skin’s
Natural pH
Neutral pH to
mildly acidic pH
cleansers that
have no impact
on steady state
pH of SC
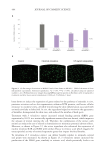
Figure 8. Technology routes to mild cleansing and moisturizing cleanser technologies.
The mechanisms by which the above type of moisturizing ingredients provide benefit from
wash-off systems vary significantly depending upon the nature of the ingredients. Since these
mechanisms are likely to be similar to their function from leave-on systems, they will be
discussed in later sections. It should be noted that there are differences between leave-on
and wash-off systems. The presence of high levels of surfactants and skin hydration under
cleansing conditions often helps to deliver certain actives rapidly into deeper layers. However,
the time of contact during cleansing is limited, and therefore the overall benefits from wash-
off systems will always be much lower than what can be expected from leave-on systems.
OTHER INGREDIENTS IN CLEANSERS
In addition to surfactants, other ingredients present in cleansers include polymers,
preservatives, pH modifiers, skin benefit agents, and fragrances.
POLYMERS
Polymers are generally used for structuring formulations, conditioning skin and hair, or for
deposition emollient and occlusive materials onto skin and hair. Polymers, because of their
high molecular weight, do not penetrate through the human SC and do not pose any major
threat to the skin barrier. Role of polymers in cosmetics has been reviewed by Lochhead,57
and a detailed review of polymers is beyond the scope of this paper. Cationic polymers
help to enhance the deposition of droplets and dispersed materials on skin and hair, as
both these surfaces are negatively charged under cleansing conditions. Polymers adsorbed
on skin and hair by themselves also can modify their wet and dry sensory and lubrication
properties. Silicone polymers, especially crosslinked silicone elastomers, are well known for
their consumer desired silky feel on skin and hair.58
Minimize Damage
Compensate for
surfactant damage
Provide posig415ve
benefits
Reduce
protein
damage
Reduce
loss of
NMFs
Reduce
lipid
damage
Mild surfactants
(Lower micellar
charge density-
large head-groups,
low acg415ve levels)
e.g. Isethionates,
Glycinates
SLES-Betaine
Combos (SLS-free),
Other aminoacid based
surfactants
Pre-saturate
surfactant
micelles with
sacrificial lipids
e.g. fag425y acids &
sterols in Bars &
Liquids
Replenish
NMFs/
humectants
Replenish
lipids
Provide
masking/
occlusion
for barrier
repair
Provide
“nutrients”/
Pro-lipids
for maintaining/
rebuilding
healthy corneum
Deposit /
deliver
Glycerol, PCA
&amino acids
during
cleansing
Deposit/
deliver
fag425y acids
&sterols
during
cleansing
Deposit
PJ/triglyceride
oils during
cleansing
Deliver
acg415ves that can
penetrate into
deeper layers &
enhance healthy
barrier rebuilding,
e.g. Esseng415al
fag425y acids,
Strategies for Mild and Moisturizing Cleanser Technologies
Maintain skin’s
Natural pH
Neutral pH to
mildly acidic pH
cleansers that
have no impact
on steady state
pH of SC
Figure 8. Technology routes to mild cleansing and moisturizing cleanser technologies.