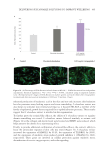
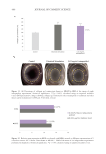
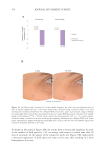
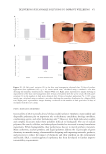
349 Aging Skin Barrier
(19) Dale BA, Resing KA, Lonsdale-Eccles JD. Filaggrin: a keratin filament associated protein. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 1985 455:330–342.
(20) Kalinin A, Marekov LN, Steinert PM. Assembly of the epidermal cornified cell envelope. J Cell Sci.
2001 114:3069–3070.
(21) Candi E, Oddi S, Terrinoni A, et al. Transglutaminase 5 cross-links loricrin, involucrin, and small
proline-rich proteins in vitro. J Biol Chem. 2001 276:35014–35023.
(22) Candi E, Schmidt R, Melino G. The cornified envelope: a model of cell death in the skin. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 2005 6:328–340.
(23) Marekov LN, Steinert PM. Ceramides are bound to structural proteins of the human foreskin epidermal
cornified cell envelope. J Biol Chem. 1998 273:17763–17770.
(24) Grove GL, Kligman AM. Age-associated changes in human epidermal cell renewal. J Gerontol.
1983 38:137–142.
(25) Leveque JL, Corcuff P de, Agache P. In vivo studies of the evolution of physical properties of the human
skin with age. Int J Dermatol. 1984 23:322–329.
(26) Marks R, Barton SP. The significance of the size and shape of corneocytes. In: Marks R, Plewig G, eds.
Stratum Corneum. New York, NY: Springer-Verlag 1983:161–170.
(27) Rougier A, Lotte C, Corcuff P, Maibach HI. Relationship between skin permeability and corneocyte size
according to anatomic site, age, and sex in man. J Soc Cosmet Chem. 1988 39:15–26.
(28) Plewig G, Scheuber E, Reuter B, Waidelich W. Thickness of corneocytes. In: Marks R, Plewig G, eds.
Stratum Corneum. New York, NY: Springer-Verlag 1983:171–174.
(29) Wertz PW, Madison KC, Downing DT. Covalently bound lipids of human stratum corneum. J Invest
Dermatol. 1989 92:109–111.
(30) Wertz PW, Swartzendruber DC, Kitko DJ, Madison KC, Downing DT. The role of the corneocyte lipid
envelopes in cohesion of the stratum corneum. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 93:169–172.
(31) Nachat R, Mechin MC, Takahara H, et al. Peptidylarginine deiminase isoforms 1–3 are expressed in the
epidermis and involved in the deimination of K1 and filaggrin. J Invest Dermatol. 2005 124:384–393.
(32) Scott IR, Harding CR. Filaggrin breakdown to water binding compounds during development of the rat
stratum corneum is controlled by the water activity of the environment. Dev Biol. 1986 115:84–92.
(33) Scott IR, Harding CR, Barrett JG. Histidine-rich protein of the keratohyalin granules. Source of the free
amino acids, urocanic acid and pyrrolidone carboxylic acid in the stratum corneum. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1982 719:110–117.
(34) Rawlings AV, Matts PJ. Stratum corneum moisturization at the molecular level: an update in relation to
the dry skin cycle. J Invest Dermatol. 2005 124:1099–1110.
(35) Rawlings AV, Scott IR, Harding CR, Bowser PA. Stratum corneum moisturization at the molecular
level. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 103:731–741.
(36) Kamata Y, Taniguchi A, Yamamoto M, et al. Neutral cysteine protease bleomycin hydrolase is essential
for the breakdown of deiminated filaggrin into amino acids. J Biol Chem. 2009 284:12829–12836.
(37) Spier HW, Pascher G. Analytical and functional physiology of the skin surface. Hautarzt. 1956 7:55–60.
(38) Cler EJ, Fourtanier A. L’acide purrolidone caboxylique (PCA) et la peau. Int J Cosmet Sci. 1981 3:101–106.
(39) Marty JP. NMF and cosmetology of cutaneous hydration. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2002 129:131–136.
(40) Harding CR, Aho S, Bosko CA. Filaggrin – revisited. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2013 35:412–423.
(41) Jokura Y, Ishikawa S, Tokuda H, Imokawa G. Molecular analysis of elastic properties of the
stratum corneum by solid-state 13C-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Invest Dermatol.
1995 104:806–812.
(42) Nakagawa N, Sakai S, Matsumoto M, et al. Relationship between NMF (lactate and potassium) content and
the physical properties of the stratum corneum in healthy subjects. J Invest Dermatol. 2004 122:755–763.
(43) Yamamura T, Tezuka T. The water-holding capacity of the stratum corneum measured by 1H-NMR. J
Invest Dermatol. 1989 93:160–164.
(19) Dale BA, Resing KA, Lonsdale-Eccles JD. Filaggrin: a keratin filament associated protein. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 1985 455:330–342.
(20) Kalinin A, Marekov LN, Steinert PM. Assembly of the epidermal cornified cell envelope. J Cell Sci.
2001 114:3069–3070.
(21) Candi E, Oddi S, Terrinoni A, et al. Transglutaminase 5 cross-links loricrin, involucrin, and small
proline-rich proteins in vitro. J Biol Chem. 2001 276:35014–35023.
(22) Candi E, Schmidt R, Melino G. The cornified envelope: a model of cell death in the skin. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 2005 6:328–340.
(23) Marekov LN, Steinert PM. Ceramides are bound to structural proteins of the human foreskin epidermal
cornified cell envelope. J Biol Chem. 1998 273:17763–17770.
(24) Grove GL, Kligman AM. Age-associated changes in human epidermal cell renewal. J Gerontol.
1983 38:137–142.
(25) Leveque JL, Corcuff P de, Agache P. In vivo studies of the evolution of physical properties of the human
skin with age. Int J Dermatol. 1984 23:322–329.
(26) Marks R, Barton SP. The significance of the size and shape of corneocytes. In: Marks R, Plewig G, eds.
Stratum Corneum. New York, NY: Springer-Verlag 1983:161–170.
(27) Rougier A, Lotte C, Corcuff P, Maibach HI. Relationship between skin permeability and corneocyte size
according to anatomic site, age, and sex in man. J Soc Cosmet Chem. 1988 39:15–26.
(28) Plewig G, Scheuber E, Reuter B, Waidelich W. Thickness of corneocytes. In: Marks R, Plewig G, eds.
Stratum Corneum. New York, NY: Springer-Verlag 1983:171–174.
(29) Wertz PW, Madison KC, Downing DT. Covalently bound lipids of human stratum corneum. J Invest
Dermatol. 1989 92:109–111.
(30) Wertz PW, Swartzendruber DC, Kitko DJ, Madison KC, Downing DT. The role of the corneocyte lipid
envelopes in cohesion of the stratum corneum. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 93:169–172.
(31) Nachat R, Mechin MC, Takahara H, et al. Peptidylarginine deiminase isoforms 1–3 are expressed in the
epidermis and involved in the deimination of K1 and filaggrin. J Invest Dermatol. 2005 124:384–393.
(32) Scott IR, Harding CR. Filaggrin breakdown to water binding compounds during development of the rat
stratum corneum is controlled by the water activity of the environment. Dev Biol. 1986 115:84–92.
(33) Scott IR, Harding CR, Barrett JG. Histidine-rich protein of the keratohyalin granules. Source of the free
amino acids, urocanic acid and pyrrolidone carboxylic acid in the stratum corneum. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1982 719:110–117.
(34) Rawlings AV, Matts PJ. Stratum corneum moisturization at the molecular level: an update in relation to
the dry skin cycle. J Invest Dermatol. 2005 124:1099–1110.
(35) Rawlings AV, Scott IR, Harding CR, Bowser PA. Stratum corneum moisturization at the molecular
level. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 103:731–741.
(36) Kamata Y, Taniguchi A, Yamamoto M, et al. Neutral cysteine protease bleomycin hydrolase is essential
for the breakdown of deiminated filaggrin into amino acids. J Biol Chem. 2009 284:12829–12836.
(37) Spier HW, Pascher G. Analytical and functional physiology of the skin surface. Hautarzt. 1956 7:55–60.
(38) Cler EJ, Fourtanier A. L’acide purrolidone caboxylique (PCA) et la peau. Int J Cosmet Sci. 1981 3:101–106.
(39) Marty JP. NMF and cosmetology of cutaneous hydration. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2002 129:131–136.
(40) Harding CR, Aho S, Bosko CA. Filaggrin – revisited. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2013 35:412–423.
(41) Jokura Y, Ishikawa S, Tokuda H, Imokawa G. Molecular analysis of elastic properties of the
stratum corneum by solid-state 13C-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Invest Dermatol.
1995 104:806–812.
(42) Nakagawa N, Sakai S, Matsumoto M, et al. Relationship between NMF (lactate and potassium) content and
the physical properties of the stratum corneum in healthy subjects. J Invest Dermatol. 2004 122:755–763.
(43) Yamamura T, Tezuka T. The water-holding capacity of the stratum corneum measured by 1H-NMR. J
Invest Dermatol. 1989 93:160–164.