473 DELIVERING SUSTAINABLE SOLUTIONS TO IMPROVE WELLBEING
Tara gum is a relatively new and underexplored galactomannan that exhibits superior
quality and performance compared to other galactomannans on the market. Its mannose-to-
galactose average ratio (M/G) of 3:1 confers its high thickening capability, good solubility,
and synergistic behavior with other hydrocolloids (Figure 20). Tara gum has been used
in the food industry as a stabilizer, thickener, and texturizer. However, its potential in
the cosmetic industry has not yet been fully explored. Because of the growing consumer
demand for natural-derived, environmental-friendly cosmetic products, more attention is
now given to this gum, especially in hair care where more than 60% of products launched
between 2019 and 2023 had ethical and environmental claims.25
Performance of starch acetate/adipate. SAA was tested in a variety of sulfated and nonsulfated
surfactant formulations (including low-percentage surfactants and more challenging sulfated
surfactants) and demonstrated outstanding performance. Results show that SAA works
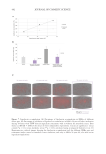
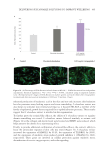
very similarly to acrylate copolymers and other market benchmarks. As seen in Figure 21,
when formulated in a traditional sulfated chassis (sodium laureth sulfate/cocamidopropyl
betaine), this polymer increases formulation viscosity and yield with increasing polymer
concentration while maintaining high clarity (low turbidity).
At these viscosities, SAA creates honey-like flow characteristics, which is desirable for
rinse-off products. The yield value allows for the suspension of many types of insoluble
ingredients with various densities.
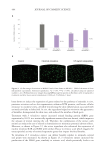
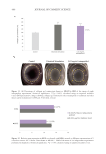
The salt response was also evaluated where varied salt concentrations were tested in a
traditional sulfated chassis (sodium laureth sulfate/cocamidopropyl betaine). The results
show that the addition of salt provides a synergistic effect, which boosts viscosity and yield
value (Figure 22).
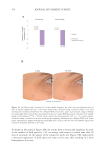
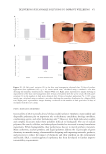
SAA was also tested in several challenging sulfate-free surfactant formulations (glutamate,
sulfonate, taurate, isethionate, and sulfosuccinate). Throughout the formulation screening,
the polymer exhibited very good performance in yield value, viscosity, and clarity at a
neutral pH. In one example, this novel ingredient was evaluated in an alpha olefin
sulfonate/cocamidopropyl betaine chassis (pH 6.5), and the results show that increasing the
Figure 20. Tara gum chemical structure.
Tara gum is a relatively new and underexplored galactomannan that exhibits superior
quality and performance compared to other galactomannans on the market. Its mannose-to-
galactose average ratio (M/G) of 3:1 confers its high thickening capability, good solubility,
and synergistic behavior with other hydrocolloids (Figure 20). Tara gum has been used
in the food industry as a stabilizer, thickener, and texturizer. However, its potential in
the cosmetic industry has not yet been fully explored. Because of the growing consumer
demand for natural-derived, environmental-friendly cosmetic products, more attention is
now given to this gum, especially in hair care where more than 60% of products launched
between 2019 and 2023 had ethical and environmental claims.25
Performance of starch acetate/adipate. SAA was tested in a variety of sulfated and nonsulfated
surfactant formulations (including low-percentage surfactants and more challenging sulfated
surfactants) and demonstrated outstanding performance. Results show that SAA works
very similarly to acrylate copolymers and other market benchmarks. As seen in Figure 21,
when formulated in a traditional sulfated chassis (sodium laureth sulfate/cocamidopropyl
betaine), this polymer increases formulation viscosity and yield with increasing polymer
concentration while maintaining high clarity (low turbidity).
At these viscosities, SAA creates honey-like flow characteristics, which is desirable for
rinse-off products. The yield value allows for the suspension of many types of insoluble
ingredients with various densities.
The salt response was also evaluated where varied salt concentrations were tested in a
traditional sulfated chassis (sodium laureth sulfate/cocamidopropyl betaine). The results
show that the addition of salt provides a synergistic effect, which boosts viscosity and yield
value (Figure 22).
SAA was also tested in several challenging sulfate-free surfactant formulations (glutamate,
sulfonate, taurate, isethionate, and sulfosuccinate). Throughout the formulation screening,
the polymer exhibited very good performance in yield value, viscosity, and clarity at a
neutral pH. In one example, this novel ingredient was evaluated in an alpha olefin
sulfonate/cocamidopropyl betaine chassis (pH 6.5), and the results show that increasing the
Figure 20. Tara gum chemical structure.