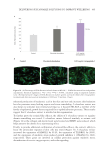
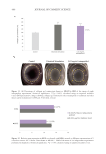
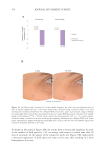
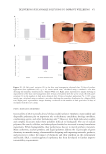
406 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
(91) Rawlings AV, Harding CR, Watkinson A, Chandar P, Scott IR, Chap 13 Leyden J, Rawlings AV, eds.
Humectants in Skin Moisturization. 1st ed. Vol 2002 2002:245–266.
(92) Juncan AM, Moisă DG, Santini A, et al. Advantages of hyaluronic acid and its combination with other
bioactive ingredients in cosmeceuticals. Molecules. 2021 26(15):4429. doi:10.3390/molecules26154429
(93) Celleno L. Topical urea in skincare: a review. Dermatol Ther. 2018 31(6):e12690. doi:10.1111/dth.12690
(94) Rawlings AV, Canestrari DA, Dobkowski B. Moisturizer technology versus clinical performance.
Dermatol Ther. 2004 17(suppl 1):49–56. doi:10.1111/j.1396-0296.2004.04s1006.x
(95) Berkey C, Kanno D, Mehling A, et al. Emollient structure and chemical functionality effects on the
biomechanical function of human stratum corneum. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2020 42(6):605–614. doi:10.1111/
ics.12656
(96) Pennick G, Harrison S, Jones D, Rawlings AV. Superior effect of isostearyl isostearate on improvement
in stratum corneum water permeability barrier function as examined by the plastic occlusion stress test.
Int J Cosmet Sci. 2010 32(4):304–312. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2494.2010.00604.x
(97) Levi K, Weber RJ, Do JQ, Dauskardt RH. Drying stress and damage processes in human stratum
corneum. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2010 32(4):276–293. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2494.2009.00557.x
(98) Harding CR, Watkinson A, Rawlings AV, Scott IR. Dry skin, moisturization and corneodesmolysis. Int
J Cosmet Sci. 2000 22(1):21–52. doi:10.1046/j.1467-2494.2000.00001.x
(99) Rawlings AV, Chapt 7. The stratum corneum and aging. In: Farage MA, Miller KW, Maibach HI, eds.
Aging of Skin. Springer-Verlag 2010:56–75. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-89656-2_7
(100) Janssens M, van Smeden J, Gooris GS, et al. Lamellar lipid organization and ceramide composition in the
stratum corneum of patients with atopic eczema. J Invest Dermatol. 2011 131(10):2136–2138. doi:10.1038/
jid.2011.175
(101) Ibid Ref. 56.
(102) Thakoersing VS, van Smeden J, Boiten WA, et al. Modulation of stratum corneum lipid composition and
organization of human skin equivalents by specific medium supplements. Exp Dermatol. 2015 24(9):669–
674. doi:10.1111/exd.12740
(103) Berkers T, Visscher D, Gooris GS, Bouwstra JA. Topically applied ceramides interact with the
stratum corneum lipid matrix in compromised ex vivo skin. Pharm Res. 2018 35(3):48. doi:10.1007/
s11095-017-2288-y
(104) SK-Influx V A Skin-Identical Lipid Concentrate for Enhanced Skin Moisturization and protectionEvonik
Goldschmidt Technical Data Sheet, D 11/07.
(105) Yarova G, Lathrop WF, Mayes AE, et al. In vivo elongation of topically applied fatty acids from a range
of different topical skincare formulations. J Cosmet Sci. May/June 2023 74(3):188–199.
(106) Zhang Q, Flach CR, Mendelsohn R, et al. Topically applied ceramide accumulates in skin glyphs. Clin
Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015 8:329–337. doi:10.2147/CCID.S83857
(107) Sahle FF, Wohlrab J, Neubert RHH. Controlled penetration of ceramides into and across the stratum
corneum using various types of microemulsions and formulation associated toxicity studies. Eur J Pharm
Biopharm. 2014 86(2):244–250. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2013.07.011
(108) Hubbard BA, Unger JG, Rohrich RJ. Reversal of skin aging with topical retinoids. Plast Reconstr Surg.
2014 133(4):481e–490e. doi:10.1097/PRS.0000000000000043
(109) Green BA, Yu RJ, Van Scott EJ. Clinical and cosmeceutical uses of hydroxyacids. Clin Dermatol.
2009 27(5):495–501. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2009.06.023
(110) Marques C, Hadjab F, Porcello A, et al. Mechanistic insights into the multiple functions of niacinamide:
therapeutic implications and cosmeceutical applications in functional skincare products. Antioxidants
(Basel). 2024 13(4):425. doi:10.3390/antiox13040425
(111) Pullar JM, Carr AC, Vissers MCM. The roles of vitamin C in skin health. Nutrients. 2017 9(8):866.
doi:10.3390/nu9080866
(112) Park SJ. A comprehensive review of topical bakuchiol for the treatment of photoaging. J Integr Dermatol.
2022:1–22.
(91) Rawlings AV, Harding CR, Watkinson A, Chandar P, Scott IR, Chap 13 Leyden J, Rawlings AV, eds.
Humectants in Skin Moisturization. 1st ed. Vol 2002 2002:245–266.
(92) Juncan AM, Moisă DG, Santini A, et al. Advantages of hyaluronic acid and its combination with other
bioactive ingredients in cosmeceuticals. Molecules. 2021 26(15):4429. doi:10.3390/molecules26154429
(93) Celleno L. Topical urea in skincare: a review. Dermatol Ther. 2018 31(6):e12690. doi:10.1111/dth.12690
(94) Rawlings AV, Canestrari DA, Dobkowski B. Moisturizer technology versus clinical performance.
Dermatol Ther. 2004 17(suppl 1):49–56. doi:10.1111/j.1396-0296.2004.04s1006.x
(95) Berkey C, Kanno D, Mehling A, et al. Emollient structure and chemical functionality effects on the
biomechanical function of human stratum corneum. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2020 42(6):605–614. doi:10.1111/
ics.12656
(96) Pennick G, Harrison S, Jones D, Rawlings AV. Superior effect of isostearyl isostearate on improvement
in stratum corneum water permeability barrier function as examined by the plastic occlusion stress test.
Int J Cosmet Sci. 2010 32(4):304–312. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2494.2010.00604.x
(97) Levi K, Weber RJ, Do JQ, Dauskardt RH. Drying stress and damage processes in human stratum
corneum. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2010 32(4):276–293. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2494.2009.00557.x
(98) Harding CR, Watkinson A, Rawlings AV, Scott IR. Dry skin, moisturization and corneodesmolysis. Int
J Cosmet Sci. 2000 22(1):21–52. doi:10.1046/j.1467-2494.2000.00001.x
(99) Rawlings AV, Chapt 7. The stratum corneum and aging. In: Farage MA, Miller KW, Maibach HI, eds.
Aging of Skin. Springer-Verlag 2010:56–75. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-89656-2_7
(100) Janssens M, van Smeden J, Gooris GS, et al. Lamellar lipid organization and ceramide composition in the
stratum corneum of patients with atopic eczema. J Invest Dermatol. 2011 131(10):2136–2138. doi:10.1038/
jid.2011.175
(101) Ibid Ref. 56.
(102) Thakoersing VS, van Smeden J, Boiten WA, et al. Modulation of stratum corneum lipid composition and
organization of human skin equivalents by specific medium supplements. Exp Dermatol. 2015 24(9):669–
674. doi:10.1111/exd.12740
(103) Berkers T, Visscher D, Gooris GS, Bouwstra JA. Topically applied ceramides interact with the
stratum corneum lipid matrix in compromised ex vivo skin. Pharm Res. 2018 35(3):48. doi:10.1007/
s11095-017-2288-y
(104) SK-Influx V A Skin-Identical Lipid Concentrate for Enhanced Skin Moisturization and protectionEvonik
Goldschmidt Technical Data Sheet, D 11/07.
(105) Yarova G, Lathrop WF, Mayes AE, et al. In vivo elongation of topically applied fatty acids from a range
of different topical skincare formulations. J Cosmet Sci. May/June 2023 74(3):188–199.
(106) Zhang Q, Flach CR, Mendelsohn R, et al. Topically applied ceramide accumulates in skin glyphs. Clin
Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015 8:329–337. doi:10.2147/CCID.S83857
(107) Sahle FF, Wohlrab J, Neubert RHH. Controlled penetration of ceramides into and across the stratum
corneum using various types of microemulsions and formulation associated toxicity studies. Eur J Pharm
Biopharm. 2014 86(2):244–250. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2013.07.011
(108) Hubbard BA, Unger JG, Rohrich RJ. Reversal of skin aging with topical retinoids. Plast Reconstr Surg.
2014 133(4):481e–490e. doi:10.1097/PRS.0000000000000043
(109) Green BA, Yu RJ, Van Scott EJ. Clinical and cosmeceutical uses of hydroxyacids. Clin Dermatol.
2009 27(5):495–501. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2009.06.023
(110) Marques C, Hadjab F, Porcello A, et al. Mechanistic insights into the multiple functions of niacinamide:
therapeutic implications and cosmeceutical applications in functional skincare products. Antioxidants
(Basel). 2024 13(4):425. doi:10.3390/antiox13040425
(111) Pullar JM, Carr AC, Vissers MCM. The roles of vitamin C in skin health. Nutrients. 2017 9(8):866.
doi:10.3390/nu9080866
(112) Park SJ. A comprehensive review of topical bakuchiol for the treatment of photoaging. J Integr Dermatol.
2022:1–22.