471 DELIVERING SUSTAINABLE SOLUTIONS TO IMPROVE WELLBEING
PART 2: RHEOLOGY MODIFIERS
Sustainability of SAA (naturally derived rheology modifier polymer). Synthetic water-soluble and
dispersible polymers play an important role as thickeners, emulsifiers, rheology modifiers,
conditioning agents, and other formulating aids.21 However, their high molecular weights
and complex structures make these polymers difficult to biodegrade. The use of natural
polymers like starch, cellulose, and other polysaccharides has increased in many formulation
ingredients. While biodegradable, their performance has yet to match synthetic materials.
Many carbomers, acrylate powders, and liquid polymers address the 12 principles of green
chemistry in manufacturing, a framework for designing and improving materials, products,
and processes to reduce the impact of chemicals and their synthesis on the environment
and health. SAA, a starch-supported copolymer, has been developed to further improve
sustainability requirements.
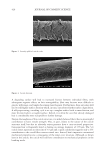
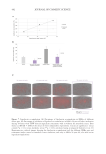
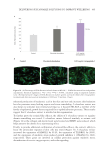
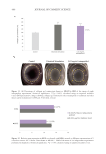
Figure 19. (A) Left panel: variation (%)in the skin tone homogeneity obtained after 28 days of product
application (low significant 0.05 p 0.1 versus initial time, calculated using a student’s t test after
checking the normality distribution by a Shapiro-Wilk test). Right panel: representative images showing an
improvement of the skin tone homogeneity after 28 days of treatment with the active cream. (B) Left panel:
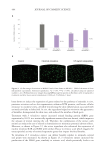
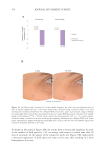
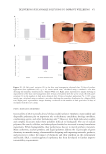
variation (%)in the number of dark spots obtained after 28 days of product application (*p 0.05 versus
initial time, calculated using a student’s t-test after checking the normality distribution by a Shapiro-Wilk
test). Right panel: representative images showing a reduction in the number of dark spots after 28 days of
treatment with the active cream.
PART 2: RHEOLOGY MODIFIERS
Sustainability of SAA (naturally derived rheology modifier polymer). Synthetic water-soluble and
dispersible polymers play an important role as thickeners, emulsifiers, rheology modifiers,
conditioning agents, and other formulating aids.21 However, their high molecular weights
and complex structures make these polymers difficult to biodegrade. The use of natural
polymers like starch, cellulose, and other polysaccharides has increased in many formulation
ingredients. While biodegradable, their performance has yet to match synthetic materials.
Many carbomers, acrylate powders, and liquid polymers address the 12 principles of green
chemistry in manufacturing, a framework for designing and improving materials, products,
and processes to reduce the impact of chemicals and their synthesis on the environment
and health. SAA, a starch-supported copolymer, has been developed to further improve
sustainability requirements.
Figure 19. (A) Left panel: variation (%)in the skin tone homogeneity obtained after 28 days of product
application (low significant 0.05 p 0.1 versus initial time, calculated using a student’s t test after
checking the normality distribution by a Shapiro-Wilk test). Right panel: representative images showing an
improvement of the skin tone homogeneity after 28 days of treatment with the active cream. (B) Left panel:
variation (%)in the number of dark spots obtained after 28 days of product application (*p 0.05 versus
initial time, calculated using a student’s t-test after checking the normality distribution by a Shapiro-Wilk
test). Right panel: representative images showing a reduction in the number of dark spots after 28 days of
treatment with the active cream.