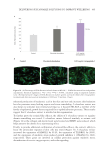
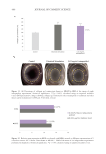
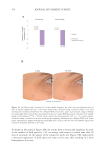
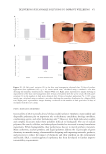
351 Aging Skin Barrier
(67) Fluhr JW, Feingold KR, Elias PM. Transepidermal water loss reflects permeability barrier status:
validation in human and rodent in vivo and ex vivo models. Exp Dermatol. 2006 15:483–492.
(68) Luebberding S, Krueger N, Kerscher M. Age-related changes in skin barrier function: quantitative
evaluation of 150 female subjects. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2013 35:183–190.
(69) Pan Y, Ma X, Zhao J, et al. The interaction of age and anatomical region influenced skin biophysical
characteristics of Chinese women. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020 13:911–926.
(70) Wilhelm KP, Cua AB, Maibach HI. Skin aging: effect on transepidermal water loss, stratum corneum
hydration, skin surface pH, and casual sebum content. Arch Dermatol. 1991 127:1806–1809.
(71) Marks R, Lawson A, Nicholls S. Age-related changes in stratum corneum structure and function. In:
Marks R, Plewig G, eds. Stratum Corneum. New York: Springer-Verlag 1983:175–180.
(72) Kligman AM. Perspectives and problems in cutaneous gerontology. J Invest Dermatol. 1979 73:39–46.
(73) Saijo S, Hashimoto-Kumasaka K, Takahashi M, Tagami H. Functional changes of the stratum corneum
associated with aging and photoaging. J Cosmet Sci. 1991 42:379–383.
(74) Hillebrand GG, Wickett RR. Epidemiology of the skin barrier: host and environmental factors in
dermatologic, cosmeceutic, and cosmetic product development. In: Roberts KW, M, eds. New York:
Informa Health Care 2008:129–156.
(75) Roskos KV, Guy RH. Assessment of skin barrier function using transepidermal water loss: effect of age.
Pharm Res. 1989 6:949–953.
(76) Luebberding S, Krueger N, Kerscher M. Age-related changes in male skin: quantitative evaluation of
one hundred and fifty male subjects. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2014 27:9–17.
(77) Akdeniz M, Gabriel S, Lichterfeld-Kottner A, Blume-Peytavi U, Kottner J. Transepidermal water loss in
healthy adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis update. Br J Dermatol. 2018 179:1049–1055.
(78) Roskos KV, Maibach HI, Guy RH. The effect of aging on percutaneous absorption in man. J
Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1989 17:617–630.
(79) Bettley FR, Donghue E. The irritant effect of soap upon the normal skin. Br J Dermatol. 1960 72:67–76.
(80) Grove GL. Age-associated changes in integumental reactivity. In: Leveque J, Agache P, eds. Aging Skin.
New York: Marcel Dekker 1993:227–238.
(81) Schwindt DA, Wilhelm KP, Miller DL, Maibach HI. Cumulative irritation in older and younger skin: a
comparison. Acta Derm Venereol. 1998 78:279–283.
(82) Cua AB, Wilhelm KP, Maibach HI. Cutaneous sodium lauryl sulphate irritation potential: age and
regional variability. Br J Dermatol. 1990 123:607–613.
(83) Robinson MK. Population differences in acute skin irritation responses. Race, sex, age, sensitive skin and
repeat subject comparisons. Contact Dermatitis. 2002 46:86–93.
(84) Bowman JP, Kligman AM, Stoudemayer T, Nicholson J. Effects of age on human cumulative irritation
responses. J Cosmet Sci. 2005 56:213–218.
(85) Ghadially R, Brown BE, Sequeira-Martin SM, Feingold KR, Elias PM. The aged epidermal permeability
barrier. Structural, functional, and lipid biochemical abnormalities in humans and a senescent murine
model. J Clin Invest. 1995 95:2281–2290.
(86) Jansen LH, Hojyo-Tomoko MT, Kligman AM. Improved fluorescence technique for estimating stratum
corneum turnover time. Br J Dermatol. 1974 90:9–11.
(87) Roberts D, Marks R. The determination of regional and age variations in the rate of desquamation: a
comparison of four techniques. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 74:13–16.
(88) Marks R. Influence of age on stratum corneum cohesion, desquamation and epidermal turnover. In:
Leveque JL, Agache P, eds. Aging Skin. New York: Marcel Dekker 1993:217–226.
(89) Engelke M, Jensen JM, Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage S, Proksch E. Effects of xerosis and ageing on
epidermal proliferation and differentiation. Br J Dermatol. 1997 137:219–225.
(90) Kreipe H, Heidebrecht HJ, Hansen S, et al. A new proliferation-associated nuclear antigen detectable in
paraffin-embedded tissues by the monoclonal antibody Ki-S1. Am J Pathol. 1993 142:3–9.
(67) Fluhr JW, Feingold KR, Elias PM. Transepidermal water loss reflects permeability barrier status:
validation in human and rodent in vivo and ex vivo models. Exp Dermatol. 2006 15:483–492.
(68) Luebberding S, Krueger N, Kerscher M. Age-related changes in skin barrier function: quantitative
evaluation of 150 female subjects. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2013 35:183–190.
(69) Pan Y, Ma X, Zhao J, et al. The interaction of age and anatomical region influenced skin biophysical
characteristics of Chinese women. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020 13:911–926.
(70) Wilhelm KP, Cua AB, Maibach HI. Skin aging: effect on transepidermal water loss, stratum corneum
hydration, skin surface pH, and casual sebum content. Arch Dermatol. 1991 127:1806–1809.
(71) Marks R, Lawson A, Nicholls S. Age-related changes in stratum corneum structure and function. In:
Marks R, Plewig G, eds. Stratum Corneum. New York: Springer-Verlag 1983:175–180.
(72) Kligman AM. Perspectives and problems in cutaneous gerontology. J Invest Dermatol. 1979 73:39–46.
(73) Saijo S, Hashimoto-Kumasaka K, Takahashi M, Tagami H. Functional changes of the stratum corneum
associated with aging and photoaging. J Cosmet Sci. 1991 42:379–383.
(74) Hillebrand GG, Wickett RR. Epidemiology of the skin barrier: host and environmental factors in
dermatologic, cosmeceutic, and cosmetic product development. In: Roberts KW, M, eds. New York:
Informa Health Care 2008:129–156.
(75) Roskos KV, Guy RH. Assessment of skin barrier function using transepidermal water loss: effect of age.
Pharm Res. 1989 6:949–953.
(76) Luebberding S, Krueger N, Kerscher M. Age-related changes in male skin: quantitative evaluation of
one hundred and fifty male subjects. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2014 27:9–17.
(77) Akdeniz M, Gabriel S, Lichterfeld-Kottner A, Blume-Peytavi U, Kottner J. Transepidermal water loss in
healthy adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis update. Br J Dermatol. 2018 179:1049–1055.
(78) Roskos KV, Maibach HI, Guy RH. The effect of aging on percutaneous absorption in man. J
Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1989 17:617–630.
(79) Bettley FR, Donghue E. The irritant effect of soap upon the normal skin. Br J Dermatol. 1960 72:67–76.
(80) Grove GL. Age-associated changes in integumental reactivity. In: Leveque J, Agache P, eds. Aging Skin.
New York: Marcel Dekker 1993:227–238.
(81) Schwindt DA, Wilhelm KP, Miller DL, Maibach HI. Cumulative irritation in older and younger skin: a
comparison. Acta Derm Venereol. 1998 78:279–283.
(82) Cua AB, Wilhelm KP, Maibach HI. Cutaneous sodium lauryl sulphate irritation potential: age and
regional variability. Br J Dermatol. 1990 123:607–613.
(83) Robinson MK. Population differences in acute skin irritation responses. Race, sex, age, sensitive skin and
repeat subject comparisons. Contact Dermatitis. 2002 46:86–93.
(84) Bowman JP, Kligman AM, Stoudemayer T, Nicholson J. Effects of age on human cumulative irritation
responses. J Cosmet Sci. 2005 56:213–218.
(85) Ghadially R, Brown BE, Sequeira-Martin SM, Feingold KR, Elias PM. The aged epidermal permeability
barrier. Structural, functional, and lipid biochemical abnormalities in humans and a senescent murine
model. J Clin Invest. 1995 95:2281–2290.
(86) Jansen LH, Hojyo-Tomoko MT, Kligman AM. Improved fluorescence technique for estimating stratum
corneum turnover time. Br J Dermatol. 1974 90:9–11.
(87) Roberts D, Marks R. The determination of regional and age variations in the rate of desquamation: a
comparison of four techniques. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 74:13–16.
(88) Marks R. Influence of age on stratum corneum cohesion, desquamation and epidermal turnover. In:
Leveque JL, Agache P, eds. Aging Skin. New York: Marcel Dekker 1993:217–226.
(89) Engelke M, Jensen JM, Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage S, Proksch E. Effects of xerosis and ageing on
epidermal proliferation and differentiation. Br J Dermatol. 1997 137:219–225.
(90) Kreipe H, Heidebrecht HJ, Hansen S, et al. A new proliferation-associated nuclear antigen detectable in
paraffin-embedded tissues by the monoclonal antibody Ki-S1. Am J Pathol. 1993 142:3–9.