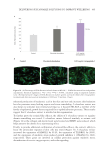
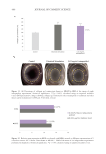
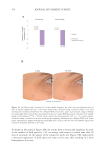
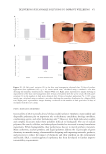
359 Sensitive skin panels
score38 and the mean BoSS score is vastly different according to the severity of sensitive
skin.39 A cut-off definition is currently in progress.
CONCLUSION
Although numerous techniques exist for sensitive skin testing, there is currently no
objective method for diagnosing sensitive skin, nor is one likely to emerge. The diagnosis
and the formation of sensitive skin panels primarily rely on questionnaires.
Another limitation is the inability to clearly differentiate normal skin from sensitive skin.
While some proposed cut-off points are helpful, it is essential to recognize that there is a
continuum ranging from completely normal skin to varying degrees of sensitive skin.
REFERENCES
(1) Misery L, Ständer S, Szepietowski JC, et al. Definition of sensitive skin: an expert position paper from
the special interest group on sensitive skin of the international forum for the study of itch. Acta Derm
Venereol. 2017 97(1):4-6. doi:10.2340/00015555-2397
(2) Misery L, Weisshaar E, Brenaut E, et al. Pathophysiology and management of sensitive skin: position
paper from the special interest group on sensitive skin of the International Forum for the Study of Itch
(IFSI). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 34(2):222-229. doi:10.1111/jdv.16000
(3) Misery L. Sensitive skins may be neuropathic disorders: lessons from studies on skin and other organs.
Cosmetics. 2021 8(1):14. doi:10.3390/cosmetics8010014
(4) Sakka M, Leschiera R, Le Gall-Ianotto C, et al. A new tool to test active ingredient using lactic acid in
vitro, a help to understand cellular mechanism involved in stinging test: an example using a bacterial
polysaccharide (Fucogel®). Exp Dermatol. 2018 27(3):238-244. doi:10.1111/exd.13489
(5) Harding AL, Murdoch C, Danby S, et al. Determination of chemical irritation potential using a
defined gene signature set on tissue-engineered human skin equivalents. JID Innov. 2021 1(2):100011.
doi:10.1016/j.xjidi.2021.100011
(6) Misery L. Irritated skin is not sensitive skin. JID Innov. 2021 1(3):10031. doi:10.1016/j.xjidi.2021.100031
(7) Brenaut E, Barnetche T, Le-Le Gall-Ianotto C, Roudot AC, Misery L, Ficheux AS. Role of the environment
in sensitive skin from the worldwide patient’s point of view: a literature review and meta-analysis. J Eur
Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 34(2):230-238. doi:10.1111/jdv.15985
(8) Frosch PJ, Kligman AM. A method of apraising the stinging capacity of topically applied substances. J
Soc Cosmet Chem. 1977 28:197-209.
(9) Honari G, Andersen RM, Maibach HI. Sensitive Skin Syndrome. 2nd ed. CRC Press 2017.
(10) Berardesca E, Fluhr JW, Maibach HI. What is sensitive skin? In: Berardesca E, Fluhr JW, Maibach HI,
eds. Sensitive Skin Syndrome. Taylor &Francis 2006:1-6.
(11) Farage MA, Katsarou A, Maibach HI. Sensory, clinical and physiological factors in sensitive skin: a
review. Contact Dermatitis. 2006 55(1):1-14. doi:10.1111/j.0105-1873.2006.00886.x
(12) Maroñas-Jiménez L, González-Guerra E, Guerra-Tapia A. Challenges of investigation. In: Honari G,
Andersen RM, Maibach HI, eds. Sensitive Skin Syndrome. 2nd ed. CRC Press 2017.
(13) Marriott M, Holmes J, Peters L, Cooper K, Rowson M, Basketter DA. The complex problem of sensitive
skin. Contact Dermatitis. 2005 53(2):93-99. doi:10.1111/j.0105-1873.2005.00653.x
(14) Green BG, Shaffer GS. Psychophysical assessment of the chemical irritability of human skin. J Soc Cosmet
Chem. 1992 43:131-147.
(15) Darlenski R, Kazandjieva J, Fluhr JW, Maurer M, Tsankov N. Lactic acid sting test does not differentiate
between facial and generalized skin functional impairment in sensitive skin in atopic dermatitis and
rosacea. J Dermatol Sci. 2014 76(2):151-153. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2014.08.014
score38 and the mean BoSS score is vastly different according to the severity of sensitive
skin.39 A cut-off definition is currently in progress.
CONCLUSION
Although numerous techniques exist for sensitive skin testing, there is currently no
objective method for diagnosing sensitive skin, nor is one likely to emerge. The diagnosis
and the formation of sensitive skin panels primarily rely on questionnaires.
Another limitation is the inability to clearly differentiate normal skin from sensitive skin.
While some proposed cut-off points are helpful, it is essential to recognize that there is a
continuum ranging from completely normal skin to varying degrees of sensitive skin.
REFERENCES
(1) Misery L, Ständer S, Szepietowski JC, et al. Definition of sensitive skin: an expert position paper from
the special interest group on sensitive skin of the international forum for the study of itch. Acta Derm
Venereol. 2017 97(1):4-6. doi:10.2340/00015555-2397
(2) Misery L, Weisshaar E, Brenaut E, et al. Pathophysiology and management of sensitive skin: position
paper from the special interest group on sensitive skin of the International Forum for the Study of Itch
(IFSI). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 34(2):222-229. doi:10.1111/jdv.16000
(3) Misery L. Sensitive skins may be neuropathic disorders: lessons from studies on skin and other organs.
Cosmetics. 2021 8(1):14. doi:10.3390/cosmetics8010014
(4) Sakka M, Leschiera R, Le Gall-Ianotto C, et al. A new tool to test active ingredient using lactic acid in
vitro, a help to understand cellular mechanism involved in stinging test: an example using a bacterial
polysaccharide (Fucogel®). Exp Dermatol. 2018 27(3):238-244. doi:10.1111/exd.13489
(5) Harding AL, Murdoch C, Danby S, et al. Determination of chemical irritation potential using a
defined gene signature set on tissue-engineered human skin equivalents. JID Innov. 2021 1(2):100011.
doi:10.1016/j.xjidi.2021.100011
(6) Misery L. Irritated skin is not sensitive skin. JID Innov. 2021 1(3):10031. doi:10.1016/j.xjidi.2021.100031
(7) Brenaut E, Barnetche T, Le-Le Gall-Ianotto C, Roudot AC, Misery L, Ficheux AS. Role of the environment
in sensitive skin from the worldwide patient’s point of view: a literature review and meta-analysis. J Eur
Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 34(2):230-238. doi:10.1111/jdv.15985
(8) Frosch PJ, Kligman AM. A method of apraising the stinging capacity of topically applied substances. J
Soc Cosmet Chem. 1977 28:197-209.
(9) Honari G, Andersen RM, Maibach HI. Sensitive Skin Syndrome. 2nd ed. CRC Press 2017.
(10) Berardesca E, Fluhr JW, Maibach HI. What is sensitive skin? In: Berardesca E, Fluhr JW, Maibach HI,
eds. Sensitive Skin Syndrome. Taylor &Francis 2006:1-6.
(11) Farage MA, Katsarou A, Maibach HI. Sensory, clinical and physiological factors in sensitive skin: a
review. Contact Dermatitis. 2006 55(1):1-14. doi:10.1111/j.0105-1873.2006.00886.x
(12) Maroñas-Jiménez L, González-Guerra E, Guerra-Tapia A. Challenges of investigation. In: Honari G,
Andersen RM, Maibach HI, eds. Sensitive Skin Syndrome. 2nd ed. CRC Press 2017.
(13) Marriott M, Holmes J, Peters L, Cooper K, Rowson M, Basketter DA. The complex problem of sensitive
skin. Contact Dermatitis. 2005 53(2):93-99. doi:10.1111/j.0105-1873.2005.00653.x
(14) Green BG, Shaffer GS. Psychophysical assessment of the chemical irritability of human skin. J Soc Cosmet
Chem. 1992 43:131-147.
(15) Darlenski R, Kazandjieva J, Fluhr JW, Maurer M, Tsankov N. Lactic acid sting test does not differentiate
between facial and generalized skin functional impairment in sensitive skin in atopic dermatitis and
rosacea. J Dermatol Sci. 2014 76(2):151-153. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2014.08.014