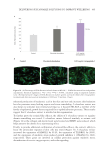
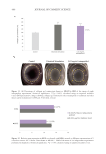
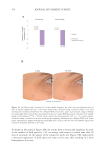
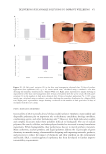
480 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
hold styling formulations. Applying polymer composite principles to fixative-treated hair
can help explain tara’s synergetic behavior with quaternized cassia. In a fiber/polymer
composite, the fibers reinforce the polymer matrix to create a stiff compound material. The
key to achieving composite properties is adhesion between the polymer and the fiber. Good
adhesion allows stress transfer from the polymer to the fibers, which prevents premature
failure of the composite. If the polymer/fiber interface (adhesion) is weak, it will dominate
the flexural properties (stiffness) of the composite.30 The flexure (three-point bend) test is
an indirect measure of the fiber/polymer adhesion,31 and the mode of failure depends on
the relative strengths of adhesion (polymer to hair) and cohesion (polymer to polymer). If
the adhesion to the hair is adequate relative to the applied stress, the cohesive properties of
the fixative polymer will contribute to the composite properties. When stress is applied to
a polymer composite, the way it dissipates depends on the balance of adhesive and cohesive
properties of the polymer.32 Even with good polymer cohesion, a polymer composite with
poor adhesion results in early failure and ultimately less stiffness. It is our hypothesis that
tara can bring cohesion to the blends while cationic cassia brings adhesion to the hair.
CONCLUSIONS
A key challenge for the beauty industry is to offer highly performing ingredients while
addressing the growing sustainability needs of the market. In this article, we presented
Table I
Summary of Sustainable Solutions
Product Technology Biodegradability
&naturality
GHG
reduction
Ecodesigned
process
Sustainable
sourcing
Performance
Tetrapeptide-1 Peptide Readily
biodegradable,
NOC*: 99,5%
-Green
chemistry
principles
Renewable
feedstocks
Upper face lifted
appearance
reduced
visibility of
wrinkles
THW biotech
ingredient
(Bacillus
ferment)
Biotech Readily
biodegradable
and 100%
natural
-Clean
fermentation
process, no
solvent
Renewable
feedstocks
Antiaging,
anti-
inflammatory,
soothing
S rebaudiana
extract
Botanical Readily
biodegradable
and 100%
natural
Energy
savings
versus
standard
extraction
process
Phenobio™
(Lubrizol,
Saucats,
France)
subcritical
water
extraction
process
Blockchain
technology
Antiaging,
anti-irritant
Starch acetate/
adipate
(SAA)
Hybrid
polymer
Inherently
biodegradable,
NOC:a 85%
Low carbon
footprint
versus
acrylates
Green
chemistry
principles
Traceable and
renewable
feedstock
Thickening,
suspension,
clarity in
cleansing
C spinosa (tara)
gum
Natural
polymer
Readily
biodegradable
and 100%
natural
Mechanical
production,
no solvent
Positive impact
on local
communities
Multifunctional
film former
and thickener
with excellent
sensory and
synergistic
behavior.
Outperforms
other gums
a NOC with water.
hold styling formulations. Applying polymer composite principles to fixative-treated hair
can help explain tara’s synergetic behavior with quaternized cassia. In a fiber/polymer
composite, the fibers reinforce the polymer matrix to create a stiff compound material. The
key to achieving composite properties is adhesion between the polymer and the fiber. Good
adhesion allows stress transfer from the polymer to the fibers, which prevents premature
failure of the composite. If the polymer/fiber interface (adhesion) is weak, it will dominate
the flexural properties (stiffness) of the composite.30 The flexure (three-point bend) test is
an indirect measure of the fiber/polymer adhesion,31 and the mode of failure depends on
the relative strengths of adhesion (polymer to hair) and cohesion (polymer to polymer). If
the adhesion to the hair is adequate relative to the applied stress, the cohesive properties of
the fixative polymer will contribute to the composite properties. When stress is applied to
a polymer composite, the way it dissipates depends on the balance of adhesive and cohesive
properties of the polymer.32 Even with good polymer cohesion, a polymer composite with
poor adhesion results in early failure and ultimately less stiffness. It is our hypothesis that
tara can bring cohesion to the blends while cationic cassia brings adhesion to the hair.
CONCLUSIONS
A key challenge for the beauty industry is to offer highly performing ingredients while
addressing the growing sustainability needs of the market. In this article, we presented
Table I
Summary of Sustainable Solutions
Product Technology Biodegradability
&naturality
GHG
reduction
Ecodesigned
process
Sustainable
sourcing
Performance
Tetrapeptide-1 Peptide Readily
biodegradable,
NOC*: 99,5%
-Green
chemistry
principles
Renewable
feedstocks
Upper face lifted
appearance
reduced
visibility of
wrinkles
THW biotech
ingredient
(Bacillus
ferment)
Biotech Readily
biodegradable
and 100%
natural
-Clean
fermentation
process, no
solvent
Renewable
feedstocks
Antiaging,
anti-
inflammatory,
soothing
S rebaudiana
extract
Botanical Readily
biodegradable
and 100%
natural
Energy
savings
versus
standard
extraction
process
Phenobio™
(Lubrizol,
Saucats,
France)
subcritical
water
extraction
process
Blockchain
technology
Antiaging,
anti-irritant
Starch acetate/
adipate
(SAA)
Hybrid
polymer
Inherently
biodegradable,
NOC:a 85%
Low carbon
footprint
versus
acrylates
Green
chemistry
principles
Traceable and
renewable
feedstock
Thickening,
suspension,
clarity in
cleansing
C spinosa (tara)
gum
Natural
polymer
Readily
biodegradable
and 100%
natural
Mechanical
production,
no solvent
Positive impact
on local
communities
Multifunctional
film former
and thickener
with excellent
sensory and
synergistic
behavior.
Outperforms
other gums
a NOC with water.