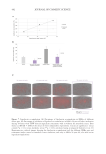
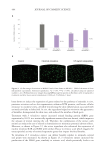
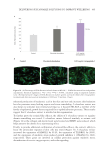
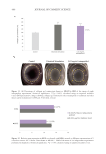
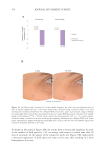
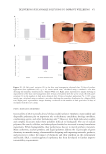
448 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
This article highlights five new commercially available technologies that meet sustainable
solution requirements while also providing exceptional performance. These technologies
include three novel active ingredients such as the Zenerity™ (Lubrizol, Brecksville, OH,
USA) biotech ingredients (INCI: glycerin, water (aqua), and bacillus ferment THW
biotech ingredient), Uplevity™ (Lipotec USA, Lewisville, TX, USA) lift peptide (INCI:
tetrapeptide-1), and Stevisse™ advanced botanical ingredients (INCI: glycerin, water
(aqua), Stevia rebaudiana leaf/stem extract), as well as two novel rheology modifiers in the
Carbopol® Fusion (Lubrizol, Brecksville, OH, USA) S-20 polymer (INCI: starch acetate/
adipate (SAA) and citric acid)and Sensomer™ (Lubrizol, Brecksville, OH, USA) tara
polymer (INCI: Caesalpinia spinosa gum tara). The resulting sustainability and performance
of these products will be discussed first for the active ingredients and then for the rheology
modifiers.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
PREPARATION OF BOTANICAL EXTRACTS:
1. Subcritical water extract of stevia leaves was prepared using an accelerated solvent
extractor (AE350, Dionex, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) under the following general conditions.
Approximately 5 g of the botanical raw material (stevia leaves) were loaded on to a
100 mL stainless steel cell along with a layer of diatomaceous earth (10 g, ASE prep DE,
Dionex). The mixture was then placed in the extractor, filled with water, and heated to
temperatures in the range of 150o-180oC under high pressure (up to 1.38 MPa) for 15
minutes to maintain subcritical water conditions. The process was repeated three times.
The combined extract was subsequently mixed with glycerin to make a 60% glycerin
solution (weight basis).
2. A hot water extract was prepared by a steeping process using 5g of the botanical raw
material and 100 mL of water. The mixture was heated and mixed at 45°C for 4 hours.
The water extract was filtered and diluted with glycerin to make a 60% glycerin solution.
The aqueous glycerin extractions were produced similarly to the hot water process but
with a 60% glycerin aqueous solution at the exact same temperature of 45°C.
ORGANIZATION FOR ECONOMIC COOPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT (OECD) 301
BIODEGRADABILITY TEST
This test guideline describes six methods that permit screening chemicals for ready
biodegradability in an aerobic aqueous medium. These methods include: the dissolved
organic content (DOC) die-away, the CO
2 evolution (modified Sturm test), the MITI (I)
(Ministry of International Trade and Industry, Japan), the closed bottle, the modified
OECD screening, and the manometric respirometry. A solution or suspension of the well
determined/described test substance in a mineral medium is inoculated and incubated
under aerobic conditions in the dark or in diffuse light. Running blanks with inoculum
but without a test substance in parallel helps to determine the endogenous activity of the
inoculum. A reference compound (aniline, sodium acetate, or sodium benzoate) is also run
in parallel to check the operation of the procedures. Normally, the test lasts for 28 days. At
least two flasks or vessels containing the test substance (plus the inoculum) and at least two
flasks or vessels containing only the inoculum should be used single vessels are sufficient
This article highlights five new commercially available technologies that meet sustainable
solution requirements while also providing exceptional performance. These technologies
include three novel active ingredients such as the Zenerity™ (Lubrizol, Brecksville, OH,
USA) biotech ingredients (INCI: glycerin, water (aqua), and bacillus ferment THW
biotech ingredient), Uplevity™ (Lipotec USA, Lewisville, TX, USA) lift peptide (INCI:
tetrapeptide-1), and Stevisse™ advanced botanical ingredients (INCI: glycerin, water
(aqua), Stevia rebaudiana leaf/stem extract), as well as two novel rheology modifiers in the
Carbopol® Fusion (Lubrizol, Brecksville, OH, USA) S-20 polymer (INCI: starch acetate/
adipate (SAA) and citric acid)and Sensomer™ (Lubrizol, Brecksville, OH, USA) tara
polymer (INCI: Caesalpinia spinosa gum tara). The resulting sustainability and performance
of these products will be discussed first for the active ingredients and then for the rheology
modifiers.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
PREPARATION OF BOTANICAL EXTRACTS:
1. Subcritical water extract of stevia leaves was prepared using an accelerated solvent
extractor (AE350, Dionex, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) under the following general conditions.
Approximately 5 g of the botanical raw material (stevia leaves) were loaded on to a
100 mL stainless steel cell along with a layer of diatomaceous earth (10 g, ASE prep DE,
Dionex). The mixture was then placed in the extractor, filled with water, and heated to
temperatures in the range of 150o-180oC under high pressure (up to 1.38 MPa) for 15
minutes to maintain subcritical water conditions. The process was repeated three times.
The combined extract was subsequently mixed with glycerin to make a 60% glycerin
solution (weight basis).
2. A hot water extract was prepared by a steeping process using 5g of the botanical raw
material and 100 mL of water. The mixture was heated and mixed at 45°C for 4 hours.
The water extract was filtered and diluted with glycerin to make a 60% glycerin solution.
The aqueous glycerin extractions were produced similarly to the hot water process but
with a 60% glycerin aqueous solution at the exact same temperature of 45°C.
ORGANIZATION FOR ECONOMIC COOPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT (OECD) 301
BIODEGRADABILITY TEST
This test guideline describes six methods that permit screening chemicals for ready
biodegradability in an aerobic aqueous medium. These methods include: the dissolved
organic content (DOC) die-away, the CO
2 evolution (modified Sturm test), the MITI (I)
(Ministry of International Trade and Industry, Japan), the closed bottle, the modified
OECD screening, and the manometric respirometry. A solution or suspension of the well
determined/described test substance in a mineral medium is inoculated and incubated
under aerobic conditions in the dark or in diffuse light. Running blanks with inoculum
but without a test substance in parallel helps to determine the endogenous activity of the
inoculum. A reference compound (aniline, sodium acetate, or sodium benzoate) is also run
in parallel to check the operation of the procedures. Normally, the test lasts for 28 days. At
least two flasks or vessels containing the test substance (plus the inoculum) and at least two
flasks or vessels containing only the inoculum should be used single vessels are sufficient