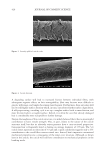
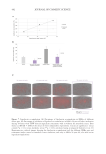
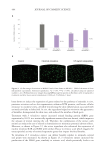
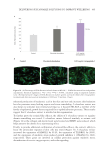
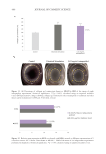
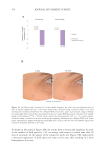
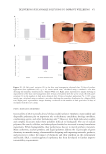
452 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
3D cultures were performed according to the following protocol: First, trypsinization
was performed on each of the petri dishes and cell suspensions were prepared. A collagen
solution was then prepared and mixed with cell suspension. 3D hydrogels with the cells in
3D were formed by crosslinking the solution at 37°C for 45 seconds. 3D structures were
separated and detached from the walls of the wells to allow gel contraction. Acellular
controls were also separated, and a warm medium was added on top of each well. Images
were taken from each well 24 hours post detachment to quantify hydrogel contraction.
An initial area was established. At t =0, all the hydrogels presented the conformation
delimited by the culture platform (24-well plate). Hydrogel contraction was quantified as
the deformation computed by surface area variation:
∆Area(at t x) (==-Ax Ai)
Ai
(Eq. 1)
Area t =0 gel → 1.86 cm2 (Area of a well in a 24-well plate)
Quantification of Area at t =x (t =24 h)
The image was analyzed with ImageJ software. The scale was configured based on the
diameter of the well (d =1.54 cm2). The diameter was simulated in ImageJ and configured
at 1.54 units. The perimeter of the hydrogel was surrounded, and the area of the hydrogel
was quantified for each image. The average for the replicates of each condition was then
calculated. Area deformation was calculated based on Eq. 1, and the data was normalized
to an absolute percent.
EVALUATION OF RETINOIC ACID PATHWAY AND SKIN REGENERATION GENES IN HUMAN
DERMAL FIBROBLASTS COCULTURED WITH HUMAN EPIDERMAL KERATINOCYTES BY RT-qPCR
HEKa and human dermal fibroblasts from adults (HDFa) were independently trypsinized
and seeded in 12-well plates. The cells in coculture were incubated at 37°C in 5% CO
2 for 24 hours. After the incubation period, the medium was removed and fresh coculture
medium was added with testing products (S rebaudiana extract at 0.001% or 0.01% and
retinoic acid at 0.001 µg/mL) prepared in the same medium. Cells treated with coculture
medium alone were used as a coculture control. After treatment, cells were incubated for an
additional 24 hours. Each condition was tested in two replicates/wells, and each test item
was assayed in six independent experiments.
For the relative quantification of gene expression levels in the retinoic acid pathway, the
cells were lysed, and the RNA was purified using a specific kit (RNeasy Mini kit) according
to the manufacture’s protocol (Qiagen). Then, RNA elution, quantification, and analysis of
the purity of the RNA samples were performed with a nanodrop Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Waltham, MA, USA). For each sample, 3 µg of high-quality RNA was retrotranscribed
with iScript Advanced (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) in a final volume of 20 µL. The
complete reaction mix was incubated in a thermal cycler (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany)
at 42°C for 30 minutes, and the reaction was stopped at 85°C for 5 minutes. Complementary
DNA was amplified using qPCR in a real-time PCR thermocycler (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA,
USA) using SYBR Green Supermix (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) in the 96-well panel
for use with SYBR® Green (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). SYBR Green binds to double-
stranded DNA molecules and emits fluorescence, which is quantified, a process where the
3D cultures were performed according to the following protocol: First, trypsinization
was performed on each of the petri dishes and cell suspensions were prepared. A collagen
solution was then prepared and mixed with cell suspension. 3D hydrogels with the cells in
3D were formed by crosslinking the solution at 37°C for 45 seconds. 3D structures were
separated and detached from the walls of the wells to allow gel contraction. Acellular
controls were also separated, and a warm medium was added on top of each well. Images
were taken from each well 24 hours post detachment to quantify hydrogel contraction.
An initial area was established. At t =0, all the hydrogels presented the conformation
delimited by the culture platform (24-well plate). Hydrogel contraction was quantified as
the deformation computed by surface area variation:
∆Area(at t x) (==-Ax Ai)
Ai
(Eq. 1)
Area t =0 gel → 1.86 cm2 (Area of a well in a 24-well plate)
Quantification of Area at t =x (t =24 h)
The image was analyzed with ImageJ software. The scale was configured based on the
diameter of the well (d =1.54 cm2). The diameter was simulated in ImageJ and configured
at 1.54 units. The perimeter of the hydrogel was surrounded, and the area of the hydrogel
was quantified for each image. The average for the replicates of each condition was then
calculated. Area deformation was calculated based on Eq. 1, and the data was normalized
to an absolute percent.
EVALUATION OF RETINOIC ACID PATHWAY AND SKIN REGENERATION GENES IN HUMAN
DERMAL FIBROBLASTS COCULTURED WITH HUMAN EPIDERMAL KERATINOCYTES BY RT-qPCR
HEKa and human dermal fibroblasts from adults (HDFa) were independently trypsinized
and seeded in 12-well plates. The cells in coculture were incubated at 37°C in 5% CO
2 for 24 hours. After the incubation period, the medium was removed and fresh coculture
medium was added with testing products (S rebaudiana extract at 0.001% or 0.01% and
retinoic acid at 0.001 µg/mL) prepared in the same medium. Cells treated with coculture
medium alone were used as a coculture control. After treatment, cells were incubated for an
additional 24 hours. Each condition was tested in two replicates/wells, and each test item
was assayed in six independent experiments.
For the relative quantification of gene expression levels in the retinoic acid pathway, the
cells were lysed, and the RNA was purified using a specific kit (RNeasy Mini kit) according
to the manufacture’s protocol (Qiagen). Then, RNA elution, quantification, and analysis of
the purity of the RNA samples were performed with a nanodrop Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Waltham, MA, USA). For each sample, 3 µg of high-quality RNA was retrotranscribed
with iScript Advanced (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) in a final volume of 20 µL. The
complete reaction mix was incubated in a thermal cycler (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany)
at 42°C for 30 minutes, and the reaction was stopped at 85°C for 5 minutes. Complementary
DNA was amplified using qPCR in a real-time PCR thermocycler (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA,
USA) using SYBR Green Supermix (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) in the 96-well panel
for use with SYBR® Green (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). SYBR Green binds to double-
stranded DNA molecules and emits fluorescence, which is quantified, a process where the