472 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
Naturality &biodegradability. SAA has a natural origin content of 85% (ISO 16128
including water) and is inherently biodegradable according to OECD 301B.
Ecodesigned process. This novel ingredient considers all 12 principles of green chemistry
in manufacturing. Specifically, the ingredient addresses principle 7 using a renewable
feedstock and principle 10 as the ingredient is inherently biodegradable.
Sustainable sourcing. The starch used comes from the potato, a traceable and renewable
feedstock. The potato is a very efficient crop (one of the highest yields per hectare on dry
content) in terms of land use and carbon footprint. According to the supplier, it does not
compete with other food in the supply chain, and it is GMO-free.
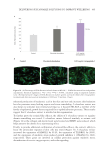
Low footprint. SAA has a 30% lower carbon footprint compared to The acrylate copolymer.
(The calculations have been conducted using various assumptions. Formulators need to
assess the impact on their finished products based on the use rate of each ingredient.) Also,
SAA is free from GMOs, does not include ethoxylated ingredients, is cold processable, and
is microbiome friendly.
Sustainability of C spinosa (tara) gum natural rheology modifier polymer. Other rheology
modifiers are also derived from natural sources like polysaccharides. Polygalactomannans
are high-molecular-weight polysaccharides that are widely used as suspending, thickening,
emulsifying, and gelling agents in applications as diverse as foodstuffs, coatings, personal
care compositions, and ingredients in oil well fracturing fluids. They are found in the
endosperm material of seeds from leguminous plants such as Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (guar
gum), C spinosa (tara gum), Ceratonia siliqua (locust bean gum), and Cassia obtusifolia
(cassia gum). A polygalactomannan is composed of the backbone of 1→4-linked β-D-
mannopyranosyl units with recurring 1→6-linked α-D-galactosyl side groups branching
from the number 6 carbon of a mannopyranose residue in the backbone. The galactomannan
polymers of the different Leguminosae species differ from one another in the frequency of the
occurrence of the galactosyl side units branching from the polymannopyranose backbone.
The average ratio of D-mannosyl to D-galactosyl units in the polygalactomannan contained
in guar gum is approximately 2:1, 3:1 for tara gum, 4:1 for locust bean gum, and 9:1 for
cassia gum. The greater the galactose side unit substitution, the greater the cold-water
solubility properties of the polygalactomannan.22,23
Sustainable sourcing. Tara gum, also known as Peruvian carob or C spinosa, is a leguminous
shrub native to Peru, South America. The fruit, usually harvested by hand, is a flat,
oblong, indehiscent, and reddish pod that contains large, round, black seeds composed of
an endosperm, germ, and hull.24 Tara seeds are obtained from local producers and have a
high social impact for the growth region.
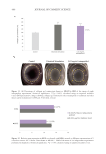
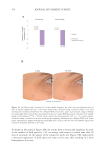
Ecodesigned process. A fully mechanical production process guarantees an environmentally
friendly and 100% natural hydrocolloid product. No solvents or chemicals are used for refining.
It is COSMOS approved, has a natural organic content of 100% (ISO 16128), is readily
biodegradable (OECD 301F), is vegan suitable, and is microbiome friendly, all of which
gives it a high-sustainability profile.
Naturality &biodegradability. SAA has a natural origin content of 85% (ISO 16128
including water) and is inherently biodegradable according to OECD 301B.
Ecodesigned process. This novel ingredient considers all 12 principles of green chemistry
in manufacturing. Specifically, the ingredient addresses principle 7 using a renewable
feedstock and principle 10 as the ingredient is inherently biodegradable.
Sustainable sourcing. The starch used comes from the potato, a traceable and renewable
feedstock. The potato is a very efficient crop (one of the highest yields per hectare on dry
content) in terms of land use and carbon footprint. According to the supplier, it does not
compete with other food in the supply chain, and it is GMO-free.
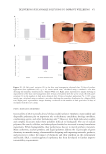
Low footprint. SAA has a 30% lower carbon footprint compared to The acrylate copolymer.
(The calculations have been conducted using various assumptions. Formulators need to
assess the impact on their finished products based on the use rate of each ingredient.) Also,
SAA is free from GMOs, does not include ethoxylated ingredients, is cold processable, and
is microbiome friendly.
Sustainability of C spinosa (tara) gum natural rheology modifier polymer. Other rheology
modifiers are also derived from natural sources like polysaccharides. Polygalactomannans
are high-molecular-weight polysaccharides that are widely used as suspending, thickening,
emulsifying, and gelling agents in applications as diverse as foodstuffs, coatings, personal
care compositions, and ingredients in oil well fracturing fluids. They are found in the
endosperm material of seeds from leguminous plants such as Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (guar
gum), C spinosa (tara gum), Ceratonia siliqua (locust bean gum), and Cassia obtusifolia
(cassia gum). A polygalactomannan is composed of the backbone of 1→4-linked β-D-
mannopyranosyl units with recurring 1→6-linked α-D-galactosyl side groups branching
from the number 6 carbon of a mannopyranose residue in the backbone. The galactomannan
polymers of the different Leguminosae species differ from one another in the frequency of the
occurrence of the galactosyl side units branching from the polymannopyranose backbone.
The average ratio of D-mannosyl to D-galactosyl units in the polygalactomannan contained
in guar gum is approximately 2:1, 3:1 for tara gum, 4:1 for locust bean gum, and 9:1 for
cassia gum. The greater the galactose side unit substitution, the greater the cold-water
solubility properties of the polygalactomannan.22,23
Sustainable sourcing. Tara gum, also known as Peruvian carob or C spinosa, is a leguminous
shrub native to Peru, South America. The fruit, usually harvested by hand, is a flat,
oblong, indehiscent, and reddish pod that contains large, round, black seeds composed of
an endosperm, germ, and hull.24 Tara seeds are obtained from local producers and have a
high social impact for the growth region.
Ecodesigned process. A fully mechanical production process guarantees an environmentally
friendly and 100% natural hydrocolloid product. No solvents or chemicals are used for refining.
It is COSMOS approved, has a natural organic content of 100% (ISO 16128), is readily
biodegradable (OECD 301F), is vegan suitable, and is microbiome friendly, all of which
gives it a high-sustainability profile.