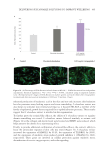
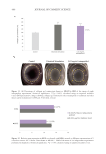
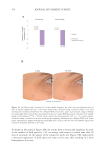
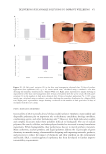
399 The Human Stratum Corneum
control actives such as the retinoid family of actives,108 AHAs (alpha hydroxyacids),109
niacinamide,110 and antioxidants such as Vitamin C.111 There are also several natural
alternatives for such benefits as Bakuchiol112 and Resveratrol.113 These actives may create
biological benefits by altering the structure of skin, and this would bring them under the
drug category. However, personal care companies limit their claims to cosmetic benefits of
such effects, which will allow them to market the products under the cosmetic category.
A detailed review of these ingredients and their impact on the SC structure is beyond the
scope of this paper, and details can be found in the refences.108–114
THE ROLE OF PH IN SKINCARE AND SKIN CLEANSING
The acid-mantle of the SC and the importance of maintaining it is well recognized in the
literature.115–118 Natural pH of a healthy SC is in the 4.5–5.0 range.119 Depending upon
the quality of skin, the pH of the SC can vary in the 4–6 range, with dry skin and atopic
skin in the 5.5–6.0 range. Infant skin at birth is close to pH 7.0 but comes to equilibrium
within a couple of weeks after birth.120
Cosmetic and personal care products in the marketplace vary in pH significantly, with
some of the acne and antiaging products at pH values as low as 3.5–4.0, to alkaline soap
bars at pH values as high as 10–11. This brings up the question of the ideal pH for leave-on
and wash-off products in skincare.
Elias and team have published extensively in this area, emphasizing the importance
maintaining the acidic pH of the SC and even suggesting that hyper-acidification of the
SC will help in rebuilding a heathier barrier.121 According to Elias and team, even a half a
unit increase in steady state pH of the SC can affect its barrier properties and the normal
regeneration of the SC barrier deleteriously. These include antimicrobial properties of
skin, enzymatic processes such as the conversion of glucosyl ceramides to ceramides, the
generation of NMFs, and the normal degradation of desmosomal linkages by proteolytic
enzymes in the SC. Changes in the antimicrobial properties of the SC can alter the skin
microbiome, which in turn can affect skin health. A renewed recognition of the importance
of the role skin pH in maintaining barrier health has led to the creation and evaluation of
products formulated under skin pH, or even hyper-acidified skin pH conditions.122
Elias et al. showed in their studies that taped-stripped mice skin recovered more rapidly
under hyper-acidification conditions compared to neutral pH conditions.121 Taking this
idea further, Blaak et al.,116 in their in vivo human studies, have further shown that the
corneum barrier in aged skin can be improved by treatment with a pH 4 lotion treatment.
In another study, Angelova-Fischer et al.122 showed that a pH 4 emulsion, compared to
a pH 5.8 emulsion, accelerated barrier recovery and enhanced the barrier integrity in
elderly subjects. In contrast to these studies, Buraczewska and Loden13 did not find any
difference between a pH 4 and a pH 7.5 leave-on cream on barrier recovery or TEWL on
SLS-challenged (sodium lauryl sulfate) skin. These findings are indeed interesting and raise
questions about the differences between SLS treated skin and naturally dry aging skin.
More studies are needed to fully validate the hypothesis that hyper-acidification indeed
will lead to superior skin barrier.
Regarding pH and skin cleansing, as mentioned earlier, the pH of products available in the
marketplace vary significantly from 3.5–11. Lately, there has been an increase in creating
cleansing products at skin pH and making implied claims that skin pH cleansers are better
control actives such as the retinoid family of actives,108 AHAs (alpha hydroxyacids),109
niacinamide,110 and antioxidants such as Vitamin C.111 There are also several natural
alternatives for such benefits as Bakuchiol112 and Resveratrol.113 These actives may create
biological benefits by altering the structure of skin, and this would bring them under the
drug category. However, personal care companies limit their claims to cosmetic benefits of
such effects, which will allow them to market the products under the cosmetic category.
A detailed review of these ingredients and their impact on the SC structure is beyond the
scope of this paper, and details can be found in the refences.108–114
THE ROLE OF PH IN SKINCARE AND SKIN CLEANSING
The acid-mantle of the SC and the importance of maintaining it is well recognized in the
literature.115–118 Natural pH of a healthy SC is in the 4.5–5.0 range.119 Depending upon
the quality of skin, the pH of the SC can vary in the 4–6 range, with dry skin and atopic
skin in the 5.5–6.0 range. Infant skin at birth is close to pH 7.0 but comes to equilibrium
within a couple of weeks after birth.120
Cosmetic and personal care products in the marketplace vary in pH significantly, with
some of the acne and antiaging products at pH values as low as 3.5–4.0, to alkaline soap
bars at pH values as high as 10–11. This brings up the question of the ideal pH for leave-on
and wash-off products in skincare.
Elias and team have published extensively in this area, emphasizing the importance
maintaining the acidic pH of the SC and even suggesting that hyper-acidification of the
SC will help in rebuilding a heathier barrier.121 According to Elias and team, even a half a
unit increase in steady state pH of the SC can affect its barrier properties and the normal
regeneration of the SC barrier deleteriously. These include antimicrobial properties of
skin, enzymatic processes such as the conversion of glucosyl ceramides to ceramides, the
generation of NMFs, and the normal degradation of desmosomal linkages by proteolytic
enzymes in the SC. Changes in the antimicrobial properties of the SC can alter the skin
microbiome, which in turn can affect skin health. A renewed recognition of the importance
of the role skin pH in maintaining barrier health has led to the creation and evaluation of
products formulated under skin pH, or even hyper-acidified skin pH conditions.122
Elias et al. showed in their studies that taped-stripped mice skin recovered more rapidly
under hyper-acidification conditions compared to neutral pH conditions.121 Taking this
idea further, Blaak et al.,116 in their in vivo human studies, have further shown that the
corneum barrier in aged skin can be improved by treatment with a pH 4 lotion treatment.
In another study, Angelova-Fischer et al.122 showed that a pH 4 emulsion, compared to
a pH 5.8 emulsion, accelerated barrier recovery and enhanced the barrier integrity in
elderly subjects. In contrast to these studies, Buraczewska and Loden13 did not find any
difference between a pH 4 and a pH 7.5 leave-on cream on barrier recovery or TEWL on
SLS-challenged (sodium lauryl sulfate) skin. These findings are indeed interesting and raise
questions about the differences between SLS treated skin and naturally dry aging skin.
More studies are needed to fully validate the hypothesis that hyper-acidification indeed
will lead to superior skin barrier.
Regarding pH and skin cleansing, as mentioned earlier, the pH of products available in the
marketplace vary significantly from 3.5–11. Lately, there has been an increase in creating
cleansing products at skin pH and making implied claims that skin pH cleansers are better