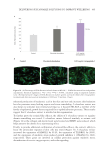
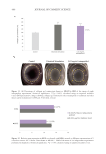
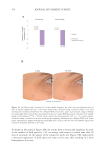
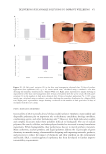
405 The Human Stratum Corneum
(71) Das R, Mallik N, Adhikari A, Bhattarai A. A comprehensive review on the creation, description, and
utilization of surfactants containing multiple hydroxyl groups. Int J Polym Sci. 2024 2024(1):Article ID
6120535. doi:10.1155/2024/6120535
(72) Bárány E, Lindberg M, Lodén M. Unexpected skin barrier influence from nonionic emulsifiers. Int J
Pharm. 2000 195(1-2):189–195. doi:10.1016/s0378-5173(99)00388-9
(73) Lémery E, Briançon S, Chevalier Y, et al. Skin toxicity of surfactants: Structure/toxicity relationships.
Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects. 2015 469:166–179. doi:10.1016/j.
colsurfa.2015.01.019.
(74) Trommer H, Neubert RHH. Overcoming the stratum corneum: the modulation of skin penetration. A
review. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2006 19(2):106–121. doi:10.1159/000091978
(75) Songkro S. An overview of skin penetration enhancers: penetration enhancing activity, skin irritation
potential and mechanism of action. Songklanakarin J Sci Technol. May-June 2009 31(3):299–321.
(76) Mitragotri S, Anissimov YG, Bunge AL, et al. Mathematical models of skin permeability: an overview.
Int J Pharm. 2011 418(1):115–129. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.02.023
(77) Moghadam SH, Saliaj E, Wettig SD, et al. Effect of chemical permeation enhancers on stratum corneum
barrier lipid organizational structure and interferon alpha permeability. Mol Pharm. 2013 10(6):2248–
2260. doi:10.1021/mp300441c
(78) Bos JD, Meinardi MM. The 500 dalton rule for the skin penetration of chemical compounds and drugs.
Exp Dermatol. 2000 9(3):165–169. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0625.2000.009003165.x
(79) Williams AC, Barry BW. Penetration enhancers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012 64:128–137. doi:10.1016/j.
addr.2012.09.032
(80) Moghadam SH, Saliaj E, Wettig SD, et al. Effect of chemical permeation enhancers on stratum corneum
barrier lipid organizational structure and interferon alpha permeability. Mol Pharm. 2013 10(6):2248–
2260. doi:10.1021/mp300441c
(80a) Ibid. Ref 77.
(81) Pham QD, Björklund S, Engblom J, Topgaard D, Sparr E. Chemical penetration enhancers in stratum
corneum—relation between molecular effects and barrier function. J Control Release. 2016 232:175–187.
doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.04.030
(82) Spada F, Barnes TM, Greive KA. Skin hydration is significantly increased by a cream formulated to
mimic the skin’s own natural moisturizing systems. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2018 11:491–497.
doi:10.2147/CCID.S177697
(83) Nisbet SJ, Dykes P, Snatchfold J. Single application of lamellar moisturizers provides significantly
increased hydration of the stratum corneum for up to 24 hours in a randomized trial. J Cosmet Dermatol.
2020 19(11):3091–3095. doi:10.1111/jocd.13361
(84) Hauser M. Cosmetic Oils in comparison: penetration and occlusion of paraffin oil and vegetable oils.
COSSMA(1-2)/y2012:26–32.
(85) Rawlings AV, Lombard KJ. A review on the extensive skin benefits of mineral oil. Int J Cosmet Sci.
2012 34(6):511–518. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2494.2012.00752.x
(86) Bosko CA, Adamus J, Bajor JS. The safety and efficacy of petrolatum. J Cosmet Sci. May/June 2022. ISSN
1525-7886 73:178-189.
(87) Ghadially R, Halkier-Sorensen L, Elias PM. Effects of petrolatum on stratum corneum structure and
function. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992 26(3 Pt 2):387–396. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(92)70060-s
(88) Chen X-W, Sun S-D, Yang G-L, Ma C-G. Engineering phytosterol-based oleogels for potential application
as sustainable petrolatum replacement. RSC Adv. 2019 10(1):244–252. doi:10.1039/c9ra06950j
(89) Barnes TM, Mijaljica D, Townley JP, Spada F, Harrison IP. Vehicles for drug delivery and cosmetic
moisturizers: Review and Comparison [review]. Pharmaceutics. 2021 13(12):2012. doi:10.3390/pharma
ceutics13122012
(90) Stortz TA, Marangoni AG. The replacement for petrolatum: thixotropic ethylcellulose oleogels in
triglyceride oils. Green Chem. 2014 16(6):3064–3070. doi:10.1039/C4GC00052H
(71) Das R, Mallik N, Adhikari A, Bhattarai A. A comprehensive review on the creation, description, and
utilization of surfactants containing multiple hydroxyl groups. Int J Polym Sci. 2024 2024(1):Article ID
6120535. doi:10.1155/2024/6120535
(72) Bárány E, Lindberg M, Lodén M. Unexpected skin barrier influence from nonionic emulsifiers. Int J
Pharm. 2000 195(1-2):189–195. doi:10.1016/s0378-5173(99)00388-9
(73) Lémery E, Briançon S, Chevalier Y, et al. Skin toxicity of surfactants: Structure/toxicity relationships.
Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects. 2015 469:166–179. doi:10.1016/j.
colsurfa.2015.01.019.
(74) Trommer H, Neubert RHH. Overcoming the stratum corneum: the modulation of skin penetration. A
review. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2006 19(2):106–121. doi:10.1159/000091978
(75) Songkro S. An overview of skin penetration enhancers: penetration enhancing activity, skin irritation
potential and mechanism of action. Songklanakarin J Sci Technol. May-June 2009 31(3):299–321.
(76) Mitragotri S, Anissimov YG, Bunge AL, et al. Mathematical models of skin permeability: an overview.
Int J Pharm. 2011 418(1):115–129. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.02.023
(77) Moghadam SH, Saliaj E, Wettig SD, et al. Effect of chemical permeation enhancers on stratum corneum
barrier lipid organizational structure and interferon alpha permeability. Mol Pharm. 2013 10(6):2248–
2260. doi:10.1021/mp300441c
(78) Bos JD, Meinardi MM. The 500 dalton rule for the skin penetration of chemical compounds and drugs.
Exp Dermatol. 2000 9(3):165–169. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0625.2000.009003165.x
(79) Williams AC, Barry BW. Penetration enhancers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012 64:128–137. doi:10.1016/j.
addr.2012.09.032
(80) Moghadam SH, Saliaj E, Wettig SD, et al. Effect of chemical permeation enhancers on stratum corneum
barrier lipid organizational structure and interferon alpha permeability. Mol Pharm. 2013 10(6):2248–
2260. doi:10.1021/mp300441c
(80a) Ibid. Ref 77.
(81) Pham QD, Björklund S, Engblom J, Topgaard D, Sparr E. Chemical penetration enhancers in stratum
corneum—relation between molecular effects and barrier function. J Control Release. 2016 232:175–187.
doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.04.030
(82) Spada F, Barnes TM, Greive KA. Skin hydration is significantly increased by a cream formulated to
mimic the skin’s own natural moisturizing systems. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2018 11:491–497.
doi:10.2147/CCID.S177697
(83) Nisbet SJ, Dykes P, Snatchfold J. Single application of lamellar moisturizers provides significantly
increased hydration of the stratum corneum for up to 24 hours in a randomized trial. J Cosmet Dermatol.
2020 19(11):3091–3095. doi:10.1111/jocd.13361
(84) Hauser M. Cosmetic Oils in comparison: penetration and occlusion of paraffin oil and vegetable oils.
COSSMA(1-2)/y2012:26–32.
(85) Rawlings AV, Lombard KJ. A review on the extensive skin benefits of mineral oil. Int J Cosmet Sci.
2012 34(6):511–518. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2494.2012.00752.x
(86) Bosko CA, Adamus J, Bajor JS. The safety and efficacy of petrolatum. J Cosmet Sci. May/June 2022. ISSN
1525-7886 73:178-189.
(87) Ghadially R, Halkier-Sorensen L, Elias PM. Effects of petrolatum on stratum corneum structure and
function. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992 26(3 Pt 2):387–396. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(92)70060-s
(88) Chen X-W, Sun S-D, Yang G-L, Ma C-G. Engineering phytosterol-based oleogels for potential application
as sustainable petrolatum replacement. RSC Adv. 2019 10(1):244–252. doi:10.1039/c9ra06950j
(89) Barnes TM, Mijaljica D, Townley JP, Spada F, Harrison IP. Vehicles for drug delivery and cosmetic
moisturizers: Review and Comparison [review]. Pharmaceutics. 2021 13(12):2012. doi:10.3390/pharma
ceutics13122012
(90) Stortz TA, Marangoni AG. The replacement for petrolatum: thixotropic ethylcellulose oleogels in
triglyceride oils. Green Chem. 2014 16(6):3064–3070. doi:10.1039/C4GC00052H