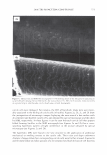
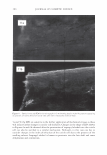
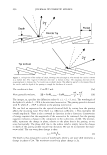
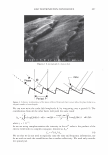
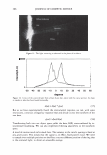
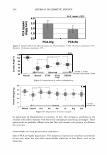
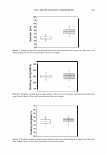
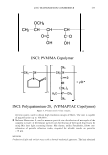
2006 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE 461 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION FORMATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF POLYELECTROLYTE MICROGEL COMPLEX There have been various names for polyelectrolyte complexes. These consist of such names as polymer-polymer complexes, or interpolyelectrolyte complexes. Despite their nomenclature as used in the academic literature they are described as two species of polymers that can interact with each other without the formation of covalent bonds. The bonds involved could be electrostatic, hydrogen bonding, Van der Waals interactions, or a combination of each. The polyelectrolyte complex used in this study is based on the electrostatic interactions of two oppositely charged molecules. It is not just a mixture of two polymers. As can be seen in Figure 6 high molecular weight linear polyanionic and polycationic polymers when combined together form a complex through the association of their opposite charges (12). There are numerous factors that should be briefly men- tioned at this point that are important in the formation of the complex. Besides con- sidering the weight ratios of the two unlike charged polymers other factors involved in the interaction are molecular weights, charge densities, pH and electrolyte content of the solvent, the solvent type, and the process· of putting the two polymers together. Since unlike charges interact on a molar basis, the stoichiometry and charge ratios are im- portant in considering their interaction. The hypothesis was that split end mending can be achieved with a polyelectrolyte complex made through the interaction of two oppositely charged polymers. This is in distinction to split end mending with a polymer-surfactant complex as patented by Ramashandran et al. (13). They invented an ingenious hair rinse composition that claimed would not only condition hair to provide such properties as wet detangling, but also lend fixative properties and repair split ends. The three main ingredients that comprised the rinse are quaternary ammonium salts (quat), water insoluble acrylic or acrylate polymers and a solvent that comprises a long chain alcohol and/or alcohol ethoxylate. The solvent is used to help compatibilize the quat and polymer. It was theorized that the quat and polymer form a complex with each other in the solvent and Polyanion Polycation - Polyelectrolyte Complex Figure 6. Ionic association of polyelectrolytes of different charge that forms a complex adapted from reference (12)_
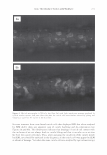
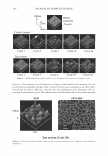
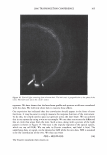
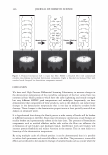
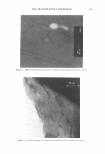
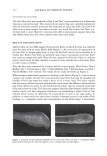
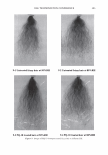
462 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE aids the deposition of the anionic polymer on the hair during the rinse cycle which would otherwise be washed away. They also theorize that split end mending is achieved by the adhesiveness of the deposited polymer which when dried forms a film that holds the splits together. Using the specialized test method as described in the methods section above allowed the screening of many types of compositions which led to the formation of the hypothesis. Some individual polymers or mixtures of polymers gave only a poor to fair mending durability efficacy. The composition discovered based on a polyelectrolyte complex was found to have increased/mending durability efficacy over control systems. The anionic polymer of this complex is PVM/MA Copolymer. The anionic contribution of this molecule depends on pH since it has two carboxylic groups per monomer unit. The cationic polymer component is Polyquaternium-28 or VP/MAPTAC Copolymer. Its cationicity is from the quaternary groups and are positively charged despite pH. The electrostatic interaction then is between the ionized carboxylic group of the anionic polymer and the quaternary nitrogen group of the cationic polymer (14). When the complex forms it can be characterized microscopically as a microgel structure. Figure 7 shows the characteristics of these microgels based on the polyelectrolyte com- plex as observed under an optical microscope at 500x. It can be observed that these particles are translucent, non-uniform in shape, and are dispersible in the aqueous Figure 7. Microgel structure as observed under optical microscope (500x)
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)