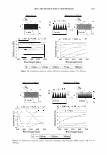
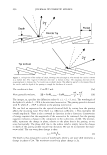
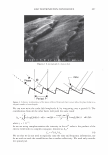
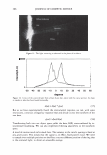
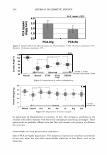
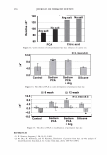
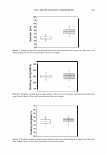
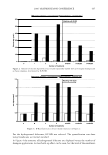
364 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 550 500 unmedullated hair 450 400 350 300 en en 250 200 en 150 100 50 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 strain(%) Figure 5. Stress-strain curves of 40 fibers of unmedullated hair. 550 500 medullated hair 450 400 350 300 - en en 250 200 en 150 100 50 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 strain (%) Figure 6. Stress-strain curves of 40 fibers of medullated hair. A series zone model has been proposed (25) to explain the behavior of hair in the yield and post-yield region. According to the series zone model, hair can be assumed to consist of two alternating zones along the microfibrils, namely the X zone and the Y zone. 30% of the a-helices in the keratin are capable of exhibiting a reversible folding-unfolding nature without breaking the disulfide bonds and these form the X zone, which charac-
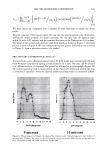
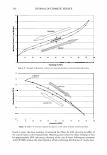
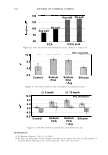
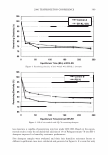
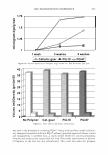
2006 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE 365 120 110- 100- E 90- � � 80- :i.... Q) 70- - $ Q) E 60- «1 :a 50- 40- 30 Figure 7. Diameters data for unmedullated (white box) and medullated hair (gray box). Box plots were obtained from 40 hair fiber measurements from each sample. ca 500- Cl.. � 400- .c - � C) C: Q) 300- :i.... - Cl) C) C: 200- :2 «1 Q) :i.... 100- cc Figure 8. Breaking strength data for unmedullated (white box) and medullated hair (gray box). Box plots were obtained from 40 hair fiber measurements from each sample. 70�------------------, 65 '#- c: 60 0 � 55 C) 5 50 a 45- C) C: :2 40- «1 � 35- .0 30...____________________. Figure 9. Breaking elongation data for unmedullated (white box) and medullated hair (gray box). Box plots were obtained from 40 hair fiber measurements from each sample.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)