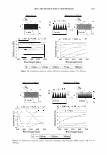
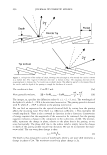
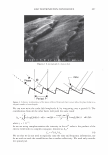
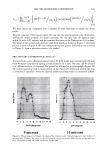
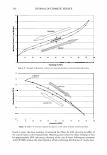
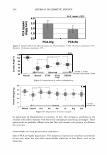
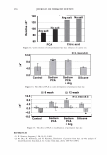
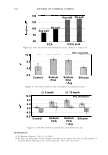
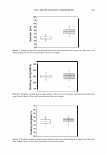
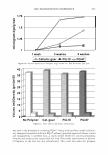
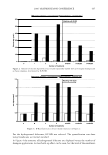
354 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 4.0 N=3, mean± S.D. CD 'i:" 3.0 � ·- J!I .. CL"T 2.0 ::::, .ea cm a.- 1.0 0.0 PCA-Arg PCA-Na Figure 8. Uptake of PCA: the effect of counter ion. PCA treatment: 5 wt%, 30 minutes immersion, 25 ° C. Recovery: 30 minutes immersion, 25 ° C. [: C J! C 0 u § 41 .c ... � "iii 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 N=20 �i I ii♦•+•-,l·•-1** : o111111 *: p0.05, **: p0.01 '1111111 Bleached --'------------------'-----------=----' Dunnett's test, control= STAG Natural Bleach STAC STAC +Ala DSDAC Figure 9. Improvement of surface hydrophobicity. 5D-�--------------------------� 10- .., __________ Bleached Q-'----�---------------------------' Natural Control Phe His Ala lie Arg Glu Figure 10. Improvement of tensile strength. ••: p0.01 Dunnett's test by application of phenylalanine or histidine. In fact, this increase is attributed to the increase of hair fiber diameter with the tensile strength per area being unchanged. These amino acids are probably diffused into hair fiber and interact with protein to influence the structure. IMPROVEMENT OF COLOR RETENTION BY SODIUM PCA Salts of PCA are highly hygroscopic. This property is expected to contribute to retention of not only water but also other water-soluble molecules in hair fibers, such as dye molecules.
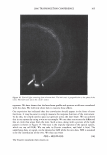
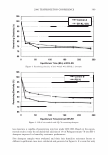
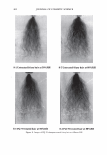
2006 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE 355 Test I was designed to examine this idea. The result is shown in Figure 11. Basically the influence of pH is significant, bur for all pH conditions better color retention was observed with PCA. The difference of color retention at pH 7.2 is impressive. Figure 12 shows the influence of counter ion on color retention effect: the combination of PCA and arginine exhibited the best. Taking the "anchor" effect of arginine into account (Figure 6), the amount of PCA in/on hair seems to be the key for the color retention effect. Test II was designed to examine the color retention effect in more practical condition. Sodium PCA was employed instead of PCA in consideration of material availability and cost aspect. Color development was significantly improved by Sodium PCA or Sodium PCA/arginine combination (Figure 13). After 6 or 12 wash cycles Yak hair treated with the PCA containing products showed a distinct brighter, more vibrant shade (Figure 14). CONCLUSION A variety of methods were applied to evaluate the interactions and effects of amino acids on bleach- or dye-treated hair. The findings obtained in this study were summarized as follows: • When amino acids are applied to hair as the state of simple aqueous solution, uptake of the amino acids is mainly controlled by ionic equilibrium. When amino acids were incorporated in hair care formulations, interaction between the amino acids and other ingredients. • Uptake of pyrrolidone carboxylic acid (PCA), a derivative of glutamic acid, is en- hanced by combining with arginine, an amino with strong affinity towards hair. • A hair conditioner incorporated with alanine improves hair surface hydrophobicity of bleach-damaged hair. • Histidine and phenylalanine improve tensile strength. • PCA was proved to be effective to improve color-retention of dyed hair. In conclusion, we emphasize the potential of amino acids as hair care material. While more than twenty specific naturally occurring amino acids are found in various proteins, only a few of them are outlined in this study. Further investigation will be required. 1 4 0.----------------------, � 120 GI ., 100 1----------------1""�-----tdlf!tt-- � 80 60 1.9 2.8 3.2 5.3 7.2 pH Value Figure 11. Color retention of semi-permanent hair dye. • PCA Citric acid
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)