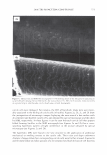
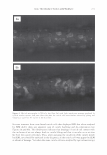
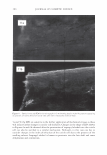
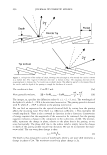
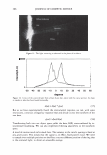
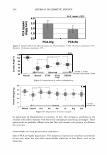
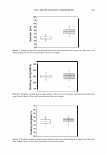
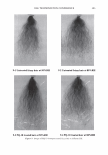
2006 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE 473 have not associated together. This is because of the steric hindrance that prevents the two macromolecules to completely associate all of their unlike charges together for complete neutralization. There are various aspects to the proposed mechanism of action of the hair repair process with the polyelectrolyte complex. First, the residual cationic charges on the microgel would tend to bind to the anionic sites of the damaged cortex through electrostatic association. To show the cationicity of the complex the anionic dye, Direct Red 80, was used as an indicator. Figure 19 shows a split end before treatment with the complex, after treatment showing mending, and after treatment with Red 80 showing a positive response to the dye. The higher level of red towards the tip indicates the predominance of complex. The red mark just prior to the split end again is the mark made with a permanent marker. During the drying stage the microgel complex is able to form a crosslinking structure which bridges the subassemblies of the fiber together. The microgel structure and its interaction with hair are illustrated in Figure 20A. The crosslinking adhesive structure of the microgel serves to glue the damaged parts of the fiber together. Since the complex is in the form of microgels in the size range of 5-10 microns they are small enough to infiltrate the fissures of the split cortex especially those as can be seen macroscopically as a split end. The smaller particles can to a certain extent permeate the lifted cuticle which is also present in damaged hair. After drying the microgels form a clear durable film which tends to bind these damaged parts of the hair together as is illustrated in A) Before treatment B) After treatment _1 ..... ..-.-.....-iiiiiiiici,iiidliiilr - C) After treatment plus Red 80 Figure 19. Anionic Direct Red 80 dye test indicates more microgel deposition on tip end.
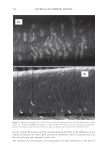
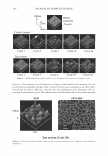
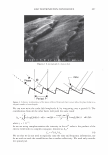
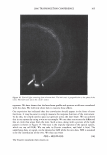
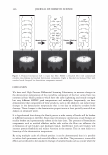
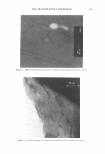
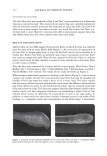
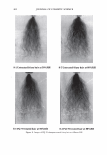
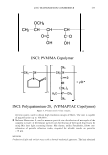
474 Microgel absorption B) JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE � - � Mendin� serum Lifted cuticle / - - .. -.,_ Split cortex 7 drying Mended hair fiber Figure 20. Proposed mechanism of split end mending. (A) Microgel crosslinking structure. (B) Binding of cuticle and split end during the drying process. Figure 20B. The unique features of the dried thin film ensure a durable mend that will survive the combing process. These various aspects of the mending mechanism provides for an efficacious level of mending that can endure a post combing process which is typical of normal styling behavior. Visual effects of this mending can be observed through SEM. In Figure 21 it can be observed that the mended fiber has a smooth cuticle where before treatment it was characterized as lifted. Also, the seam of the weld is evident where the split end used to be. Having an increased understanding of the formation and chemistry of polyelectrolyte complexes and their interaction with the chemistry and morphology of hair allows the design of new compositions that could function in the same way as the complex studied here. CONCLUSIONS Hair styling trends have created a need for hair repair compositions that will attempt to restore damaged hair co its normal state. Split ends are one manifestation of that damage. A test method has been devised that can assess in a realistic fashion the mending of split ends through various treatment regimens. The method is realistic in that the tagged split end fibers are part of a tress that can be subjected to normal combing or washing cycles. With this method it has been discovered that a polyelectrolyte complex can semi-permanently mend split ends in that split end hair treated with this composition can survive the stress of combing. The composition is efficacious especially in compari- son to a commercial benchmark with a split end mending claim. A proposed mechanism of action has been put forth and consists of the microgel structure of the polyelectrolyte complex acting as a crosslinking structure in the damaged subassemblies of the damaged fiber. The understanding of this mechanism opens the way for the development of new
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)