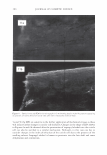
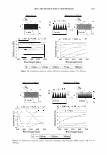
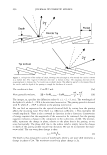
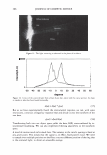
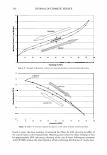
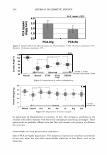
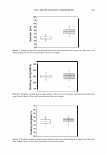
298 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Um = �I exp[j(cf(x) - nKx)]dx. (5) We evaluate U m using our phase function. The round-trip phase shift due to depth is 0 at x = 0, and maximum (2a) at x P. It is also linear. Substituting explicitly into equation 5 yields: p p Um = H exp[j(2et(x/p)- nKx)]dx = H exp[j(et - m1r): ]dx (6) 0 0 2( 1 ) {exp[j2(u - m,r)]-1 }. u - m1T Multiplying by the complex conjugate yields the intensity 1 1 U*mum = {1 - cos2(a - m1r)} = 2 {1 - cos(2a)} (7) 2(a - m,r)2 2(a - m,r) 1 . 2 = sm (a). (u - m,r)2 We show a plot of this function for the significant orders in Figure 4. The relative intensities of the various orders at a specific depth are shown in Figure 5. 1 � 0.9 -� 0.8 - "iii 0.7 e o.6 i 0.5 -I--:-=-�-:--:,-������...........,_----+-.......,_�� � 0.4 - -� 0.3 S 0.2 --t--'----.----:-'¼-���--�---,.....:.......�--=--� C Q .1 -·I-----''-:--------""'--�.,,,..,._-.--�.-�� 0 __ .1,,,aii��!!lilllli,..�==ir,::��:.,,c,,;.iiii,,aa..-;.;,�;..ilii 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 depth (microns) - - order a - - - - order 1 -order-1 -order2 - - - order 3 -order-3 --order4 Figure 4. The relative amplitude of the various orders as a function of a.. For a reasonable hair a. = 10 should correspond to a depth of about 1 micron. Notice that different orders peak at different depths and that at specific depths all the light is contained in a single order. This is the basis of blazing. Almost no light is found in negative orders.
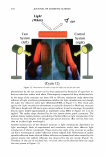
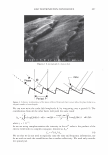
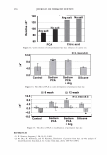
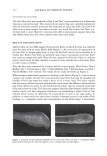
2006 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE 299 Intensity f -••- lntens ity I Shift (degrees) Figure 5. At specific depths energy is distributed amongst a number of orders, at other depths the grating is blazed for the wavelength of interest and all the energy is contained in a single order. The position of the orders is set by the mean periodicity of the grating. Ablation will increase facet spacing variability. EXPERIMENT AL SIMULATION Real experiments use lasers with Gaussian beam shapes the illumination optics has a finite beam divergence, and the detector has finite aperture size. This means that the signal is really a convolution of the diffraction pattern with real system artifacts. THE DIFFRACTED ORDERS ARE SPATIALLY INCOHERENT WITH EACH OTHER The first issue that needs to be addressed is mixing between orders. We note that the orders exit at different angles from the sample (nominally with 4 degree separations). This means that the outgoing plane waves, that are the orders, will be tilted with respect to each other. Many fringes will appear across the photosensitive surface. This means that the orders will not be spatially coherent at the detector, and any cross beating terms will explicitly cancel. We can add the intensities of the orders incoherently. THE LASER HAS A GAUSSIAN BEAM SHAPE The laser beam profile is Gaussian, and as such its properties are well known. We can assume that the minimum waist is at the hair (z = 0) and that the electric field propagates as E(r,z) = E0 11 �:) exp [ - 11 � :) 2] exp [ - j( kz - arctan ( :J + 2�:)) ]- (S a )
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)