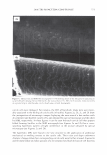
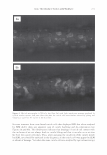
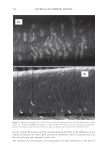
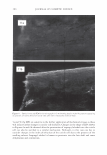
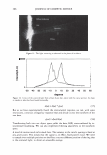
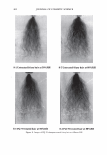
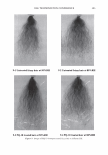
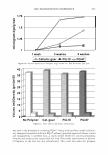
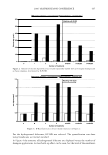
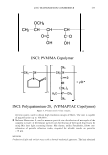
454 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE polymer systems were tested for their ability to mend split ends. The experimentation evolved from testing individual polymers to polymer blends where it was discovered that a polyelectrolyte complex, formed between the ionic interactions of two oppositely charged polymers, provided positive effects in the mending process. The novel compo- sition was found to have durability to a post combing treatment and was still able to be washed off the hair after a post shampoo treatment. Based on these features it was characterized as a semi-permanent hair repair effect. Besides a description of the poly- electrolyte complex used in this study, as well as test results, a proposed theory of the mechanism of mending is described. This mechanism serves as a model for designing other complexes that will have the same hair mending effect. MATERIALS AND METHODS MATERIALS Natural brown hair tresses are supplied by International Hair Importers and are made with their patented swatching process to be 3.5 grams of loose hair, 6.5 inches in length from the bottom of the sewn end to the tip of the hair, and 1 3/4 inches across. Brand of combs used in the experiments are Sally's Beauty Supply. Fine teeth section of the comb contains eight teeth per centimeter. The free acid form of the copolymer of methyl vinyl ether and maleic anhydride (INCI: PVM/MA Copolymer) is supplied by International Specialty Products under the trade name Gantrez® S-97 BF Polymer. The copolymer of vinyl pyrrolidone and methacryl- amidopropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride (VP/MAPTAC Copolymer INCI: Polyquaternium-28) is supplied by International Specialty Products under the trade name Conditioneze® NT-20. This is a 20% (w/w) solution in water. These ingredients are used as supplied and not purified or modified in any way. Figure 3 illustrates the structures of these compounds. A commercial product with a split end mending claim was used as a benchmark. Its' ingredient label is: Aqua/Water, Cyclopentasiloxane, Propylene Glycol, Hydroxypropyl Guar, Phenoxyethanol, Peg 40 Hydrogenated Castor Oil, PEG/PPG-17/18 Dimethi- cone, Behentrimonium Chloride, Aminomethyl Propanol, Trideceth-12, Polyquate- rium-4, Dimethiconol, Limonene, Linolool, Benzyl Salicylate, Amodimethicone, Alpha- Isomethyl Ionene, Perea Gratissima/Avocado Oil, Carbomer, Potato Starch Modified, Methyl Paraben, Butylphenyl Methylpropional, Citronella!, Cetrimonium Chloride, Laureth-23, Laureth-4, Prunus Armeniaca/Apricot Kernel Oil, Coumarin, Hexyl Cin- namol, Parfum/Fragrance, F.I.L. Cl638713 EQUIPMENT • Nikon SMZ 1500 Stereomicroscope • Linksys 2.2 program for digital imagery (Linksys for Windows, Linkam Scientific Instruments Inc., 8 Epsom Downs Metro Center, Waterfield, Tadsworth, Surrey, KT205HT, U.K.) • Thermal/Mechanical Styling Apparatus custom built at ISP to produce tresses with split ends. • Amray model 1820/D digital Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) with a LaB6
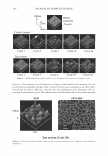
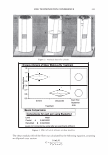
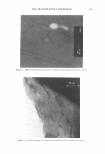
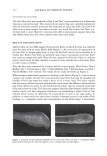
2006 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE OCH3 I CH 2 -CH-CH--CH--- I I O=C C=O I I OH OH INCi: PVM/MA Copolymer n 455 INCi: Polyquatemium-28, (VP/MAPT AC Copolymer) Figure 3. Polymers used to form complex. electron source, used to obtain high resolution images of fibers. The unit is capable of magnification up to 100,000x. • Malvern Mastersizer S, used to measure particle size distribution of microgels of the complex in water. It determines particle size distribution of the liquid dispersions by using Mie laser light scattering theory. Mie theory, unlike Fraunhofer, allows con- sideration of particle refractive index, required for reliable results on particles l0µm. METHODS Production of split ends on hair tresses with a thermal-mechanical apparatus. The hair obtained
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)