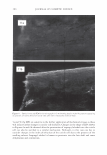
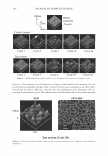
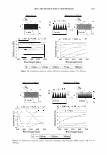
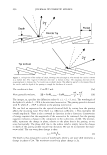
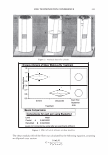
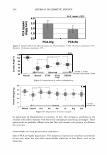
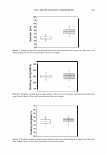
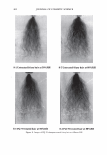
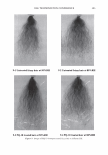
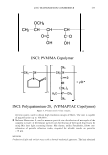
464 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE DESIGN-EXPERT Plot Phase Behavior • Design Points Phase Behavior = 1.564 Run #81 0.50 0.38 X: A: Polyquatemium-28 = 1.80 Y: 8: PVM/MA Copolymer = 0.20 Solution Character Legend: 1 = Milky 2 = Very hazy 3 = Hazy 4 = Slightly hazy 5 = Clear ... C1I E , o 0.25 i � ci::i 0.13 0.00 0.00 2.44 • • • • • Complex Tested • • 4.88 7.31 A: Polyquatemium-28 Figure 9. Phase behavior of polymers of differing charge. • • • • 9.75 contained the complex, but with further investigation under the microscope it was observed that all dispersions other than the clear ones contained microgels. It was concluded that the white opaque dispersions then had the highest intensity of microgels formed and would be most appropriate for testing the split end mending benefit. The complex tested in this study is identified in Figure 9 and consists of two percent active complex made by combining PVM/MA Copolymer and Polyquaternium-28 at a weight ratio of 0.2 to 1.8 respectively. Polyelectrolyte complexes based on other anionic and cationic polymer combinations were studied in this way but have not been tested for mending efficacy. Complexes using PVM/MA Copolymer as the anionic component have been formed with Polyquaternium- 7, 10, and 11. Also, Vinylpyrrolidone/acrylates/laurylmethacrylate copolymer serving as the anionic polymer has been complexed with Polyquaternium-28. The phase diagram built in Figure 9 is based on weight ratios of the two polymers. However, the two polymers are actually interacting on a stoichiometric basis through their charge interaction. To further elucidate the interaction of these two polymers the following study was conducted and is illustrated in Figure 10. Various levels on a weight basis of Polyquaternium-28 were combined with 0.2% PVM/MA Copolymer. The resultant viscosity was measured using a Brookfield viscometer with a small sample adapter and the viscosity plotted against the calculated mole ratio of cationic monomer to anionic monomer. The shape of the curve is distinctly parabolically curved containing a minimum viscosity. It was discovered that this minimum of viscosity occurs at a
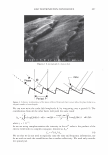
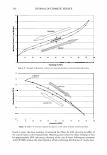
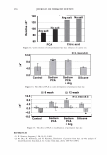
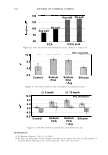
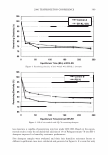
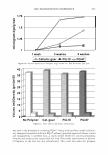
2006 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE 1000 - -------------------� c.. 100 u Excess polyanions Excess polycations ----· ------- 465 - � • PVM/MA 0.2% r/J 0 u .!? 10 1 0.00 0.50 1.00 1.50 2.00 2.50 3.00 3.50 4.00 4.50 5.00 Unit mole ratio of Polyquaternium-28 to PVMIMA Copolymer Figure 10. Dependence of viscosity on unit mole ratio cationic to anionic groups. stoichiometric charge ratio of one to one where the stoichiometric equivalence of cationic and anionic charges are the same. This indicated a maximum in the amount of microgels formed since these are discrete particles that are dispersed in solution. Polymer ratios deviating away from the one to one stoichiometric equivalence would contain polymer not associated in a microgel and would increase the viscosity of the solution. The lower viscosity evident for the 1: 1 ratio was due to the hydrodynamic volume of the complexed chains being smaller than when free un-complexed polymers are present in solution at other charge ratios. This charge-charge interaction contributes to the compact nature of the microgel structure of the complex and exemplified the stoichiometric interaction of the two polymers. It was determined that the complex chosen to repair split ends has a cationic to anionic charge ratio of precisely 1.14. MENDING TEST RESULTS OF MICROGEL COMPOSITION A screening study showed the efficacy of the polyelectrolyte complex in split end mending durability. The control systems were based on the component polymers of the complex used alone and a clear 1: 1 mixture of the two polymers where there are no discrete microgels present. All polymer and polymer combinations were kept constant at a total of 2.00% active. This screening study consisted of measuring twenty tagged fibers for each formulation instead of the usual one hundred and was based on complete mending as observed with a magnifying glass. Test results showed that the complex had increased durability of mending over the control formulations. Test results are in Table III. When the complex was used alone at 2.00% active in a one hundred fiber study it mended 92 out of 100 fibers after treatment and before combing. After combing the tress twenty times 68 fibers remained mended. When the 2.00% active complex was formulated into a simple lotion formula thickened with Xanthan Gum approximately
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)