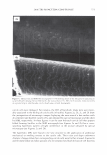
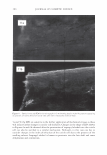
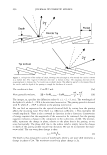
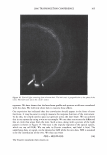
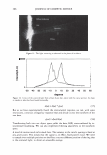
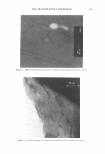
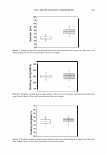
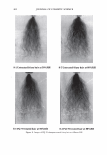
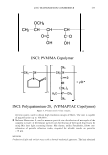
462 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE aids the deposition of the anionic polymer on the hair during the rinse cycle which would otherwise be washed away. They also theorize that split end mending is achieved by the adhesiveness of the deposited polymer which when dried forms a film that holds the splits together. Using the specialized test method as described in the methods section above allowed the screening of many types of compositions which led to the formation of the hypothesis. Some individual polymers or mixtures of polymers gave only a poor to fair mending durability efficacy. The composition discovered based on a polyelectrolyte complex was found to have increased/mending durability efficacy over control systems. The anionic polymer of this complex is PVM/MA Copolymer. The anionic contribution of this molecule depends on pH since it has two carboxylic groups per monomer unit. The cationic polymer component is Polyquaternium-28 or VP/MAPTAC Copolymer. Its cationicity is from the quaternary groups and are positively charged despite pH. The electrostatic interaction then is between the ionized carboxylic group of the anionic polymer and the quaternary nitrogen group of the cationic polymer (14). When the complex forms it can be characterized microscopically as a microgel structure. Figure 7 shows the characteristics of these microgels based on the polyelectrolyte com- plex as observed under an optical microscope at 500x. It can be observed that these particles are translucent, non-uniform in shape, and are dispersible in the aqueous Figure 7. Microgel structure as observed under optical microscope (500x)
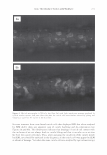
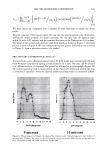
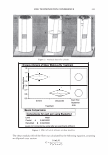
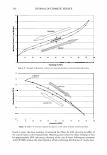
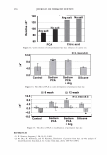
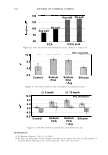
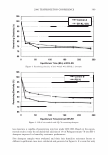
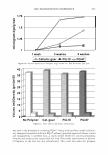
2006 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE 463 solvent. Stability shows that a 4% active complex dispersion is stable at elevated tem- peratures and multiple freeze thaw cycles. The particles are in the range of 5-10 microns in size as measured with a Malvern particle size analyzer. The particle size distribution is illustrated in Figure 8. By studying the phase diagram formed between PVM/MA Copolymer and Polyquater- nium-28 the phase regions of their interactions were identified. In building this phase diagram various weight ratios were used in putting the two polymers together while keeping other variables constant. The variables kept constant were the solvent which was water, pH of the PVM/MA Copolymer which was adjusted to 7 .00 ± 0.05, and the type of polymer which inherently controls the molecular weight and other intrinsic properties of the polymers such as cationic charge density. The process of putting the two polymers together was also kept constant. The character of the polymer combinations were noted and given a value against set criteria. The phase diagram was produced by regression analysis with the help of statistical software (15 ). The resultant phase diagram is illus- trated in Figure 9. The complexes were characterized macroscopically by appearance where the value of 5 was given to clear solutions, 1 was given to opaque white disper- sions, and 2 through 4 for intermediate values for solution characters see legend in Figure 9. It was first thought that the opaque milky white dispersions designated 1 only Yablefl') .-�-,.._ ................ .....-----1 1.D mo "DI.II '11111..D Figure 8. Malvern particle size analysis of microgel structure. 'I) D
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)