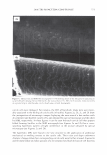
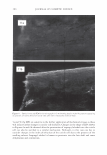
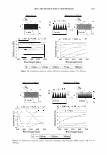
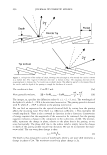
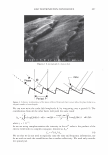
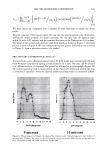
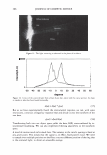
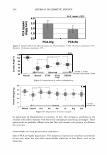
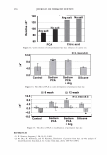
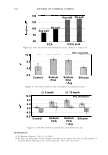
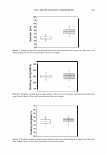
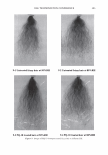
2006 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE Monolayer � qi' n 0 = 1.00, n 1 = 1.45, n2 = 1.55 ,......., 5 � ------ E..... 4 --·-· 0 ·····....... -· --- :� 3 - w:: . ...., .. ,,,----· --=---.-.-.......--- ---------- - --- --------- Q.) c;::::: (IJ 0 380 480 580 680 780 Wavelength [nm] Mono layer/EMA /Jo = /J1 = 0.5 ------------------- -: n l ---- �qi' /J, d l ' ----� Cuticle 380 480 580 680 780 Wavelength [nm] Id· -Onm --25nm, -·-50nm' ---·75nm, ........... JOOnm I . ' Figure 10. Simulation study on surface reflection, monolayer model, d :'5 100 nm. Mono layer/EMA Multilayer/EMA �qi' � qi' 291 n ' 1 n ' 1 ----- -- -------: d-1�==;.�==��=� i' ' ---- n 0 = 1.00, n/ = 1.23, n 2 = 1.55 5�------- � Cuticle n 0 = 1.00--H 1 = 1.45, n 2 = 1.55 5 -- - -- - --- .... d=0nm � 4 f--- - - - ------, .£ 3 .::: � 2 t+:::: �1 -.:..-.-a.--...e.-:--::..-=-•-.c..:-· =-.-.-.-.-.-·-. o��������� 480 580 680 780 380 480 580 680 780 Wavelength [nm] Wavelength [nm] I d: - lOOnm, - - -200nm, -· - 300nm I Figure 11. Simulation study on surface reflection, monolayer and multilayer EMA model, 100 :'5 d :'5 300 nm.
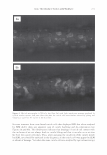
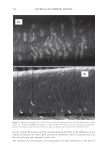
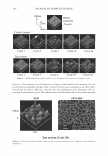
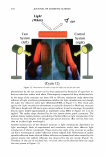
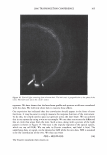
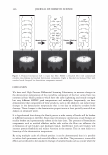
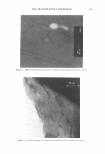
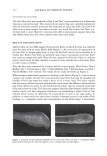
292 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Light (White) � eye �/ . .---- � ....-- , - . -.. � -- -,,.,_ -- .. .. ------ � ,__ . -· .,_ Test Control i.ri?-'�-�� -, -�� �-� ,. . (Cycle 12) Figure 12. Observation of surface supecular reflection on red dyed hair. phenomenon by the test system can be thus explained by formation of super-low re- fractive index hair surface with about 50nm asperity composed of fatty alcohol and air. In the range of the structure size from 100 to 300 nm, simulation study shows that influence of light interference phenomenon inhibits the light introduction even though the super low refractive index layer (Monolayer/EMA in Figure 11). This result goes against the light introduction phenomena as typically observed in Moth-eye structure (200 nm in height and 300 nm in space uneven surface). In such a size range, the gradual density layers model (approximated as multilayer using EMA in Figure 11) is to be applied. The surface shape obtained by the test system shows gentle curvatures. The gradual density model predicts a possibility of further effective light introduction if the structure has more heights with enough high special densities. (But still has finer sizes than an incident light wavelength.) Another characteristic of the obtained structure is light introduction dependence on light wavelength. Both of experimental and simulation results show effective light introduction of shorter wavelength. Those results also imply a fine structure on surface can bias a wavelength of surface reflection toward reddish shift. Observation of surface specular reflection shows whitish diffuse reflection on human head when treated by the control system, but reddish reflection was observed by the test system (Figure 12). Therefore, in the case of red dyed hair, vivid red color can be observed from any angle (the test system in Figure 13 ).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)