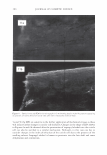
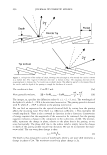
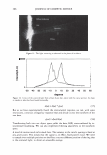
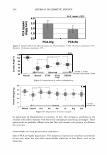
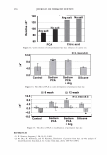
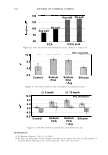
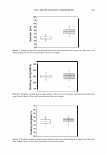
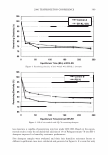
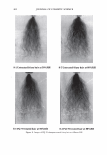
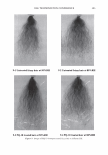
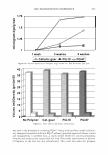
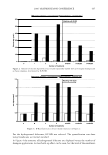
]. Cosmet. Sci.! 58, 421-434 CTuly/August 2007) New high-charge density hydrophobically modified cationic HEC polymers for improved co-deposition of benefit agents and serious conditioning for problem hair T. V. DROVETSKAYA, E. F. DIANTONIO, R. L. KREEGER, J. L. AMOS, and D. P. FRANK, Amerchol Corporation, A Subsidiary of The Dow Chemical Company, 171 River Road, Piscataway, NJ 08854. Synopsis A series of new high charge density Polyquaternium-671 (PQ-67) polymers have been prepared and evaluated in shampoo formulations. These new compositions represent an addition to the family of high- viscosity quaternized hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) polymers with cationic substitution of trimethyl am- monium and dimethyldodecyl ammonium2 (Figure lA) described in (l) and (2). The evaluation protocol included objective lab methods and subjective panel studies on different hair types. Commercial condi- tioning polymers: PQ-67 (Polymers SoftCAT1M�'') and cationic guar4 Qaguar C-13S®5) were used as per- formance benchmarks. It was found that increasing the cationic charge density of the PQ-67 polymers above 1.45 meq/g (equiva- lent of 2 weight-percent (wt.%) nitrogen) resulted in a several-fold boost of their co-deposition ability. These experimental, high charge density PQ-67 polymers were shown to deliver silicones and other per- formance ingredients from shampoo formulations more efficiently than any other polymer currently avail- able on the market for rinse-off hair cleansing/conditioning applications. The polymers also provided improved wet and/or dry conditioning, volume control, and could be instrumental in achieving sleek looking hair and improved control/manageability of unruly or frizzy hair. The high charge density PQ-67 polymers are also ideally suited for highly-fragranced surfactant-based formulas that are used in aroma- therapy and spa products due to their superior ability to deliver fragrance. BACKGROUND Hair is a diverse substrate that comes in different shapes, colors and textures. Its properties and appearance vary for different races and age groups, as do the benefits that consumers are seeking in new hair care products. As more and more consumers are shampooing, grooming, coloring, bleaching or waving/straightening their hair, they are Address all correspondence to T. V. Drovetskaya. 1 Hydrophobically modified cationic conditioning HEC polymers. 2 Supplied by Amerchol Corporation/Dow Chemical Company under the trade name SoftCAT™ SL and SK. 3 Supplied by Amerchol Corporation/Dow Chemical Company. 4 Guar hydroxypropyltrimonium chloride. 5 Supplied by Rhodia. 421
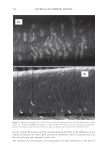
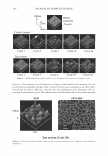
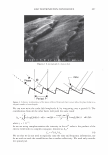
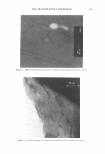
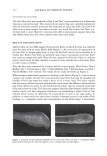
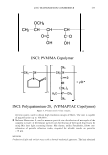
422 A. PQ-67 ( JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE o"-)n { ? H PH (CH2CHP)x (CH2CHj Hz·H CH 3�·CH3 Cl C12H25 Figure 1. Cationic conditioning HEC polymers. also damaging it, and thus the need for products that can mitigate and repair this damage is increasing dramatically. The current offering of cationic conditioning poly- mers is quite broad and is expanding, with HEC-based polymers representing a signifi- cant portion of this market. Varying structural parameters of these polymers, such as molecular weight, cationic and hydrophobic substitution and/or the degree of ethox- ylation significantly impacts their performance on hair and creates the much needed diversity of properties and benefits. This paper describes the impact of the charge substitution (CS) in combination with the hydrophobic substitution (HS) on the depo- sition properties and overall conditioning of PQ-67 polymers. New compositional fea- tures enhanced the performance of the experimental high charge density PQ-67 poly- mers, which were found superior when compared to any of the competitive benchmarks used in this study in deposition of performance ingredients and for overall conditioning. This performance makes the new structures a valuable addition to the family of cationic conditioning polymers. These polymers were found to be especially useful to manage hair types that benefit from volume control and extra-conditioning, such as unruly, difficult-to-manage hair or for Asian hair types. 6 RES UL TS AND DISCUSSION POLYMER COMPOSITION New experimental high charge density PQ-67 polymers belong to the family of high viscosity quaternized hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) derivatives with cationic substitu- tion of trimethyl ammonium and dimethyldodecyl ammonium (Figure lA) described in (1) and (2) and recently commercialized for personal care applications by Amerchol Corporation and the Dow Chemical Company under the trade name of Polymers Soft- CAT™ SL and SK. Similar to the commercially available grades, experimental PQ-67 samples described in this paper were produced by reacting HEC polymers with 3-chloro- 2-hydroxypropyldodecyldimethyl ammonium chloride and 2,3-epoxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride in aqueous isopropanol (2). In this work we used polymers made of a high viscosity HEC with the degree of ethoxylation similar to one of commercially 6 We are currently in progress evaluating performance of experimental high charge density PQ-67 polymers on Asian hair.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)