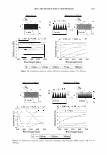
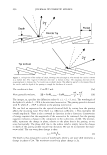
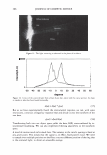
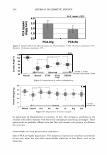
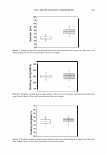
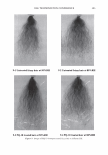
... "ii .c DJ :-::: rn E l! DJ e u E 1000 800 600 400 200 2006 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE UCARE SoftCA T SoftCAT PQ-67 PQ-67 JR-30M SK-MH SK-H %N- 2.1 %N-2.5 429 Cat. Commercial guar 2-in-1 shampoo Figure 6. Silicone deposition from Shampoo Formulation B on European virgin brown hair. treated with Shampoo Formulation B was measured following the procedure described above. Polymers PQ-10 (UCARE™ JR-30M), PQ-67 (SoftCAT™ SK-MH and H), and cationic guar CTaguar C-13S®) were used as benchmarks. A market leading commercial shampoo product that had an SLES/DSLSS/CAPB surfactant base, dimethiconol, and guar hydroxypropyl trimethylammonium chloride listed on the ingredient label was also included in the study as an additional benchmark. The results obtained for the silicone deposition from each formulation are presented in Figure 6. It has been found that the PQ-10 polymer with medium-high cationic charge (UCARE™ JR-30M, %N -1.8) and PQ-67 polymer with medium cationic charge (SoftCAT™ SK-H, 1.45 wt.% N) out- performed cationic guar n the prototype formulation B. They yielded silicone deposition in the range of -430 and 490 micrograms of silicone per gram of hair, respectively, which was close to the amount delivered by the commercial shampoo product that listed an SLES/DSLSS/CAPB surfactant system and cationic guar: -460 micrograms of silicone. Experimental high charge density PQ-67 polymers described in this paper delivered significantly more silicone (-850 and 1,100 micrograms, respectively, depending on the CS) showing again a significant increase in silicone deposition over the benchmarks. Subjective panel evaluation on tresses. In order to further validate the outstanding conditioning performance of the high charge density PQ-67 polymers in the prototype Shampoo Formulation B, a sample shampoo containing one of these polymers (-2.1 wt.% N, medium HS) was compared to the market-leading commercial shampoo used in the silicone deposition study (Figure 7 A). Pairs of European virgin brown hair tresses were prepared as described above and distributed to panelists. The hair was evaluated for wet/dry comb and feel properties. According to the results presented in Figure 7 A, the panelists preferred the prototype Formulation B containing a high charge density PQ-67 polymer over the commercial shampoo for both wet comb (9110)2° and feel (8/10). 21 20 Exact significance level = 98% (binomial distribution). 21 Exact significance level = 89% (binomial distribution).
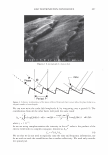
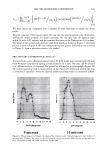
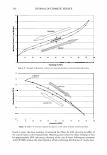
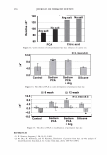
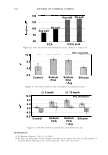
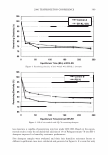
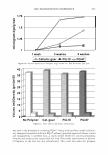
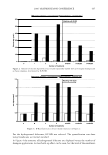
430 10 .!! ca 6 CL .. 4 2 ::I z 0 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 10 8 6 4 2 0-+--L--__,..._..__...,._____...,.______...,. Wet Comb Wet Feel Dry Comb Dry Feel Wet Comb Wet Feel Dry Comb Dry Feel I 1':111 Commercial shampoo ■ PQ-67, 2.5 wt. % N, Medium HS II lll::ll Cationic guar □ PQ-67, 2.1 wt % N, Medium HS I Figure 7. Subjective panel evaluation on European virgin hair. A. Shampoo Formulation B: PQ-67 versus commercial shampoo. B. Shampoo Formulation B: PQ-67 versus cationic guar. After the hair dried, panelists' choices indicated no statistical difference in d ry comb and feel between swatches (Figure 7 A). A second panel study was conducted to compare the Shampoo Formulation B made with a high charge density PQ-67 polymer22 to an identical formulation containing cationic guar.23 As expected from the silicone depo- sition data, the PQ-67 formulation outperformed the guar control in both comb and feel in the wet and dry state, Figure 7B. DEPOSITION OF FRAGRANCE Fragrance is another important performance ingredient besides silicones that greatly contributes to the overall aesthetics of shampoo products and their acceptance by con- sumers. Delive ry of long-lasting fragrance to the hair from rinse-off formulations such as shampoos and conditioners represents a serious challenge. The high charge density PQ-67 polymers that demonstrated remarkable performance in assisting the deposition of silicones on hair were also tested for deposition of fragrance from a shampoo formu- lation. White Tea Fragrance24 was formulated at 1 wt.% in an SLES/DSCADA 25 pro- totype shampoo formulation along with 0.4 wt.% cationic conditioning polymer. The fragrance deposition from a shampoo containing a high charge density PQ-67 polymer26 was evaluated against similar shampoos containing no polymer, SoftCAT SK-MH,27 and cationic guar in a series of subjective panel evaluation studies on European virgin hair tresses conducted in the same manner as described above. The results of these studies are summarized in Figure 8. It was shown that the high charge density PQ-67 polymer used in this study improved deposition of the white tea fragrance on virgin brown hair and that the difference was perceivable to the panelists in all three cases (9/1028 or 8/1029). 22 PQ-67 polymer with 2.1 wt. %N and medium HS was used in this study. 2 ' Jaguar C-13S. 24 Provided by Fragrance Resources, Inc. 25 The same surfactant system as used in the Shampoo Formulation A. 26 PQ-67 polymer with 2.5 wt.% N and medium HS. 2 7 SoftCAT SK-MH was found to deliver more fragrance on skin from rinse-off formulations compared to other PQ-67 and PQ-10 polymers and cationic guar (SoftCA T SK Conditioning Polymers, product brochure issued by Amerchol Corporation/Dow Chemical Company (2005)). 2 8 Exact Significance level = 98% (binomial distribution). 29 Exact Significance level = 89% (binomial distribution).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)