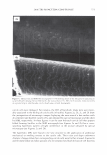
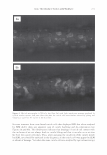
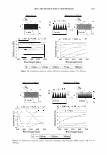
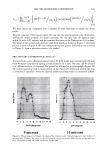
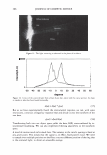
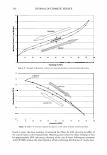
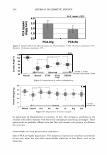
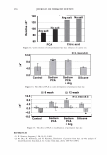
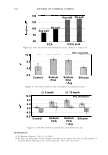
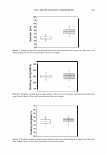
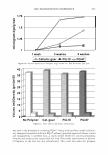
ca D.. 2006 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE 335 � 1.5 +---------------''-..il.:---........,.......c-- _ _ _ _______ _ _____ ___ --t CIJ ::, :i -0 0 ... cu Cl) .c U) o---------------------,------------------- 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Humidity(% RH) Figure 7. Effect of humidity on the shear modulus of untreated and bleached hair. fiber. Therefore, we see a higher shear modulus compared to the untreated fiber at low humidities (below 55% RH). Above 55% RH these salt linkages become weak and therefore the shear modulus goes below that of the unbleached (untreated) fibers. Sorption-Hysteresis. Figure 8 is an example of the hysteresis effect for untreated hair measured gravimetrically. Hysteresis at a given RH is the difference in the moisture content between the desorption (where moisture content is decreasing) and the sorption curves (where moisture content is increasing). Sorption hysteresis reflects the ability of the hair to retain moisture. Figure 9 shows the shear modulus of untreated hair as a function of relative humidity. The data indicated by "ST ART" were collected after the untreated hair sample was thoroughly dried and the line connects the data as the humidity was incremented upwards. Unlike the gravimetric response to moisture sorption, the shear modulus is substantially reduced as moisture is absorbed. Upon reaching almost 90% RH, the humidity was decreased by the same steps and the shear modulus increases. The two curves show the sorption hysteresis measured by a mechanical method involving shear modulus measurements. The shear modulus curve for desorption lies below that for sorption, indicating that the moisture content is higher (shear modulus lower) in the desorption mode at a given humidity as observed in Figure 8. CONCLUSIONS On a theoretical basis, torsion measurements are dominated by the periphery of hair fibers allowing sensitivity to factors affecting the cuticle layer. Cuticle abrasion was
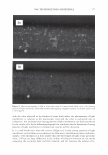
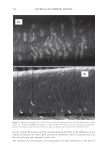
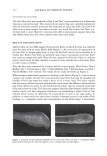
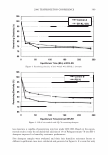
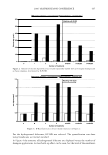
336 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 30 25 i 20 · � 15 C C 0 10 ·s 5 :!!! 0 -5 Humidity (% RH) Figure 8. Example of hysteresis of moisture sorption-desorption measured gravimetrically. 1.5 1.4 1.3 1.2 � 1.1 0 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Humidity (%RH) Figure 9. Effect of moisture sorption-desorption on the shear modulus of untreated hair. found to lower the shear modulus of untreated hair fibers by 40% showing the effect of the cuticle layer in this measurement. Bleaching also lowers the shear modulus of hair by approximately 40% indicating softening of the cuticle layer. Subsequent treatment with CETAB increases the shear modulus of hair indicating fortification of cuticle layer.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)