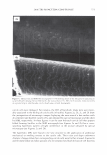
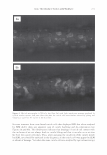
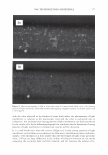
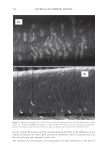
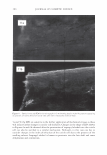
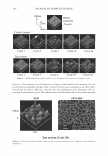
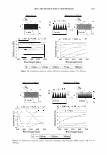
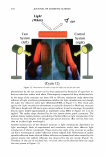
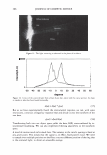
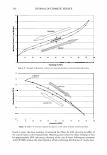
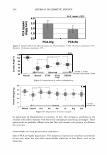
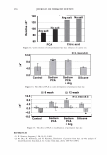
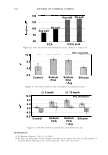
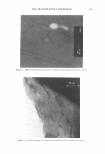
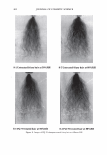
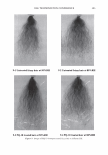
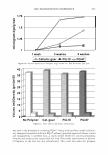
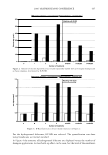
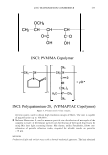
2006 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE 367 Porous medulla leaves hair less uniform leading to broader distributions of tensile mechanical properties. The cavities of the medulla could act as defects which affect the mechanical properties but do not interfere in the crystalline character of the fiber. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors acknowledge financial support of FAPESP (Funda�ao de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado de Sao Paulo, Grant 04/13066-0) and of CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Pesquisa, Grant 471061/2004-2). RDCW acknowledges a FAPESP fellowship (Grant 03/13436-0). REFERENCES (1) J. R. Smith, A quantitative method for analyzing AFM images of the outer surfaces of human hair,]. Microsc., 191, 223-228 (1998). (2) J. A. Swift and J. R. Smith, Atomic force microscopy of human hair, Scanning, 22, 310-318 (2000). (3) P. Hallegot, R. Peteranderl, and C. Lechene, In-situ imaging mass spectrometry analysis of melanin granules in the human hair shaft,]. Invest. Dermatol, 122, 381-386 (2004). (4) J. R. Smith and J. A. Swift, Maple syrup urine disease hair reveals the importance of 18- methyleicosanoic acid in cuticular delamination, Micron, 36(3), 261-266 (2005). (5) I. M. Kempson, W. M. Skinner, and P. K. Kirkbride, Calcium distributions in human hair by TOF- SIMS, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1624, 1-5 (2003). (6) L. N. Jones, M. Simon, N. R. Watts, F. P. Booy, A. C. Steven and D. A. D. Parry, Intermediate filament structure: hard a-keratin, Biophys. Chem., 68, 83-93 (1997). (7) S. Naito, K. Arai, M. Hirano, N. Nagasawa, and M. J. Sakamoto, Crosslinking structure of keratin. V. Number and type of crosslinks in microstructures of untreated and potassium cyanide treated human hair, Appl. Polym. Sci., 61, 1913-1925 0996). (8) S. Naito and K. Arai, Type and location of SS linkages in human hair and their relation to fiber properties in water,]. Appl. Polym. Sci., 61, 1918-2113 (1996). (9) J. R. Smith and J. A. Swift, Lamellar subcomponents of the cuticular cell membrane complex of mammalian keratin fibres show friction and hardness contrast by AFM, J. Microsc., 206, 182-193 (2002). (10) K. Roper, J. Fohles, D. Peters, and H. Zahn, Morfological composition of the cuticle from chemically treated wool. 1. Calculating endocuticle content in isolated cuticle from results of amino-acid analysis, Text. Res.]., 54, 139-143 (1984). (11) E. G. Bendit and M. Feughelman (Eds.), "Keratin," Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology, 8th Ed., Chapter 1 (1967). (12) A. Kelch, S. Wessel, T. Will, R. Hintze, R. Wepf, and R. Wiesendanger, Penetration pathways of fluorescent dyes in human hair fibres investigated by scanning near-field optical microscopy, J. Microsc., 200(3), 179-186 (2000). (13) L. Pi.ietsh and M. R. Moeller, On pathways for small molecules into and out of human hair fibers,]. Forensic Sci., 41(1), 121-125 (1996). (14) L. Kreplak, A. Franbourg, F. Briki, F. Leroy, D. Dalle J., and Doucet, A new deformation model of hard alpha-keratin fibers at the nanometer sacale: implications for hard alpha-keratin intermediate filament mechanical properties, Biophys. ]., 82, 2265-2274 (2002). (15) D. W. Deedrick, Microscopy of Hair Part 1: A Practical Guide and Manual for Human Hairs, Forensic Sci. Commun., 1(6) (2004). (16) L. Kreplak, F. Briki, Y. Duvault, J. Doucet, C. Merigoux, F. Leroy, L. Leveque, L. Miller, G. L. Carr, G. P. Williams, and P. Dumas, Profiling lipids across Caucasian and Afro-American hair transverse cuts, using synchroton infrared microspectrometry, Int. J. Cosmet. Sci., 23, 369-374 (2001). (17) G. Mahrle and C. E. Orfanos, The spongious keratin and the medulla of human scalp hair, Arch. Derm. Res., 241, 305-316 (1971). (18) S. Nagase, S. Shibuichi, K. Ando, E. Kari ya, and N. Satoh, Influence of internal structures of hair fiber
368 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE on hair appearance. I. Light scattering from the porous structure of the medulla of human hair,]. Cosmet. Sci., 53(2), 89-100 (2002). (19) H. Zahn, P. Jolles, and H. Hocker, Formation and Structure of Human Hair (Birkhauser Verlag, Basel, Switzerland), pp. 59, 148 (1997). (20) J. A. Swift, Fundamentals of Human Hair Science (Micelle Press, Weymouth, Dorset), pp. 57 (1997). (21) M. S. C. Birbeck and E. Mercer, The electron microscopy of the human hair follicle. The hair cuticle, ]. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 3, 223-233 (1957). (22) J. L. Clement, A. Le Pareux, and P. F. Ceccaldi, Contribution a l'etude de la medulla des poils, Ann. Dermatolog. Venereoly, 108, 849-857 (1981). (23) Rogers, G. E., Electron microscope studies of hair and wool, Ann. New York Acad. Sci., 83, 378-399 (1959). (24) S. M. Thozhur, A. D. Crocombe, and P.A. Smith, Structural characteristics and mechanical behaviour of beard hair,]. Mater. Sci., 41, 1109-1121 (2006). (25) Feughelman, M., A two-phase structure for keratin fibers, Text. Res.]., 29, 223 (1959). (26) M. Feughelman, A model for the mechanical properties of the alpha-keratin cortex, Text. Res.]., 64, 236-239 (1994). (27) B. M. Chapman, A mechanical model for wool and other keratin fibers, Text. Res.]., 1102-1109 (1969).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)